Parameter Estimation of Two Spiking Neuron Models With Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithms
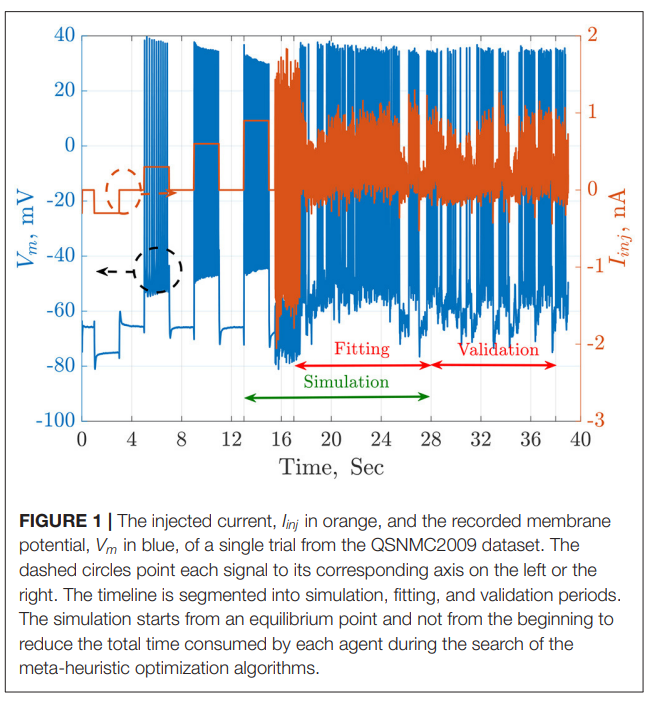
The automatic fitting of spiking neuron models to experimental data is a challenging problem. The integrate and fire model and Hodgkin–Huxley (HH) models represent the two complexity extremes of spiking neural models. Between these two extremes lies two and three differential-equation-based models. In this work, we investigate the problem of parameter estimation of two simple neuron models with a sharp reset in order to fit the spike timing of electro-physiological recordings based on two problem formulations. Five optimization algorithms are investigated; three of them have not been used to
Chaos-Based RNG using Semiconductor Lasers with Parameters Variation Tolerance
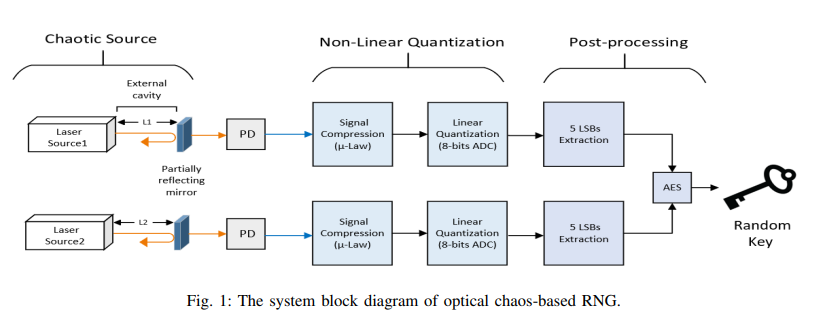
Random numbers play an essential role in guaranteeing secrecy in most cryptographic systems. A chaotic optical signal is exploited to achieve high-speed random numbers. It could be generated by using one or more semiconductor lasers with external optical feedback. However, this system faces two major issues, high peak to average power ratio (PAPR) and parameter variations. These issues highly affected the randomness of the generated bitstreams. In this paper, we use a non-linear compression technique to compand the generated signal before it is quantized to avoid the effects of the PAPR. Also
An application of ELECTRE III to contractor selection
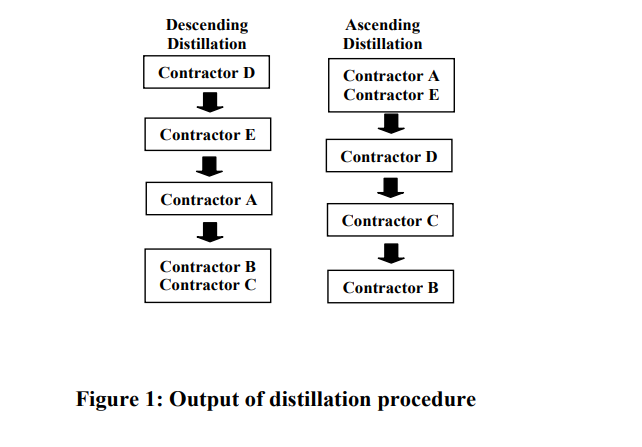
Contractor selection is carried out in order to choose a competent and capable contractor to do the work. To help in this selection, baselines are established to ensure that the contractors have the required skills, resources, and abilities to execute the project. Contractor selection is a multiple criteria decision making wherein several criteria are required to be evaluated simultaneously. This paper proposes a decisionmaking model for contractor selection utilizing ELECTRE III modeling. The steps of ELECTRE III model include; estimation of concordance indices, estimation of discordance
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 61

