Heating and Freezing Injury to Plant Tissues and Their Effect on Bioimpedance: Experimental Study
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) has been used as a technique for the assessment of food attributes. This paper discusses the effect of injuries caused by heating and freezing treatments to plant's bioimpedance. Unlike other studies to these kinds of injuries, experiments are carried out on the whole fruit using non-invasive electrodes keeping the plant tissues unharmed. Moreover, one of the samples under test was chosen to be a ripening fruit to discuss how its bioimpedance behavior differ from non-ripening ones. The experimental results showed how the damage caused by freezing
Mathematical analysis of gene regulation activator model
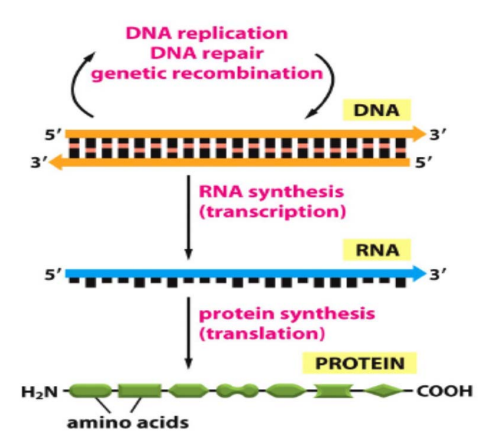
This paper presents a complete analysis of the mathematical model of the gene regulation process. The model describes the induced gene expression under the effect of activators. The model differential equations are solved analytically, and the exact solution of the gene model is introduced. Moreover, a study of the model dynamics, including the fixed points and stability conditions are presented. The parameters effects on the phase plane portraits and the transient responses of the mRNA as well as the protein concentrations are intensively detailed. This work serves as a brick stone towards a
Frational Order Inverse Filters Based on CCII Family
This paper proposes two generalized topologies of fractional order inverse filters (FOIF). All possible realizations of each topology are investigated using the second generation current conveyor (CCII) family. Inverse fractional highpass (IFHPF), inverse fractional bandpass (IFBPF), and inverse fractional lowpass (IFLPF) filters are realized using the same topology based on the generalized admittances. Numerical and P-Spice simulation results are presented for selected cases to approve the theoretical findings. The fractional order parameters increase the design flexibility and
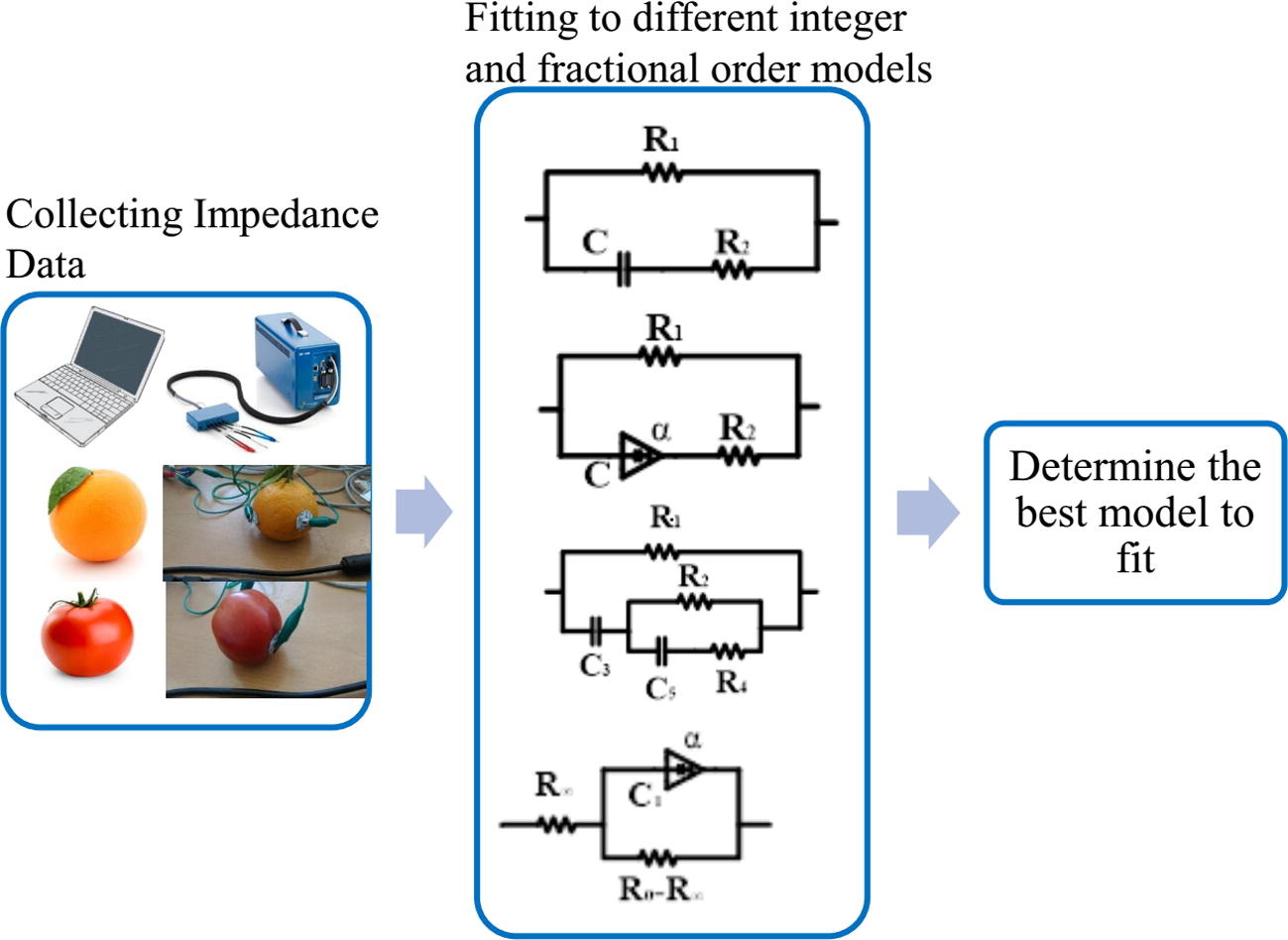
Experimental comparison of integer/fractional-order electrical models of plant
In this paper, different integer and fractional-order models are studied from electrical point of view, these models are used to fit the measured impedance data for different types of fruits and vegetables. Experimental work is done on eight different models for six types of fruits to verify the best fitting model. Electric impedance is measured in the range of frequencies (200 mHz–200 Khz) using a non-destructive method, where the tissues are not damaged by electrode insertion. Moreover, two integer order models have been extended to the fractional order domain where data analysis and fitting
Study of Energy Harvesters for Wearable Devices
Energy harvesting was and still an important point of research. Batteries have been utilized for a long time, but they are now not compatible with the downsizing of technology. Also, their need to be recharged and changed periodically is not very desirable, therefore over the years energy harvesting from the environment and the human body have been investigated. Three energy harvesting methods which are the Piezoelectric energy harvesters, the Enzymatic Biofuel cells, and Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are being discussed in the paper. Although Biofuel cells have been investigated for a
Study of fractional flux-controlled memristor emulator connections
In this paper, the series and parallel connections of the fractional flux-controlled memristors are studied. Asymmetric I-V hysteresis with high I-V nonlinearity can be obtained from single fractional memristor as reported in literature. However, connecting different memristor emulators can convert the asymmetric hysteresis to symmetric one and maintaining the high I-V nonlinearity to be used in some memristor devices. The proposed circuits have been analyzed mathematically to study the effect of changing the frequency and fractional power. Different cases have been verified on PSpice using
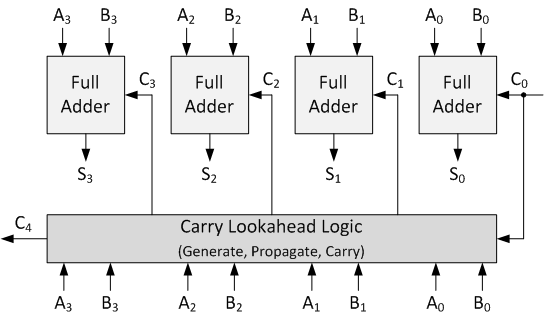
N-digits ternary carry lookahead adder design
Carry lookahead adders (CLAs) are extensively used in digital circuits due to their logarithmic computational time (O(log n)) compared to linear computational time(O(n)) in the ripple carry adders. In this paper, two design approaches for N-digits ternary logic CLA based on K-map and threshold logic methods are proposed in addtion to their realization using CNTFETs only and memristor with CNTFETs. Finally, 4-bit ternary CLA is presented. A comparison and tradeoffs among the proposed designs are presented in terms of the delay and the area. The comparison shows that the transistor-only-based
Incremental Grounded Voltage Controlled Memristor Emulator
Memristor has become an interesting research subject in the recent years. Its special behavior has attracted the attention of the research community that motivated researchers to investigate it in details. As memristor is a relatively new electrical element, it is not yet available in the market as a solid state component Researchers found their way to build memristor emulators to achieve its pinched hysteresis. While many papers proposed floating emulators, only a few papers presented a grounded one. In this paper, an incremental grounded memristor emulator is proposed. The mathematical model
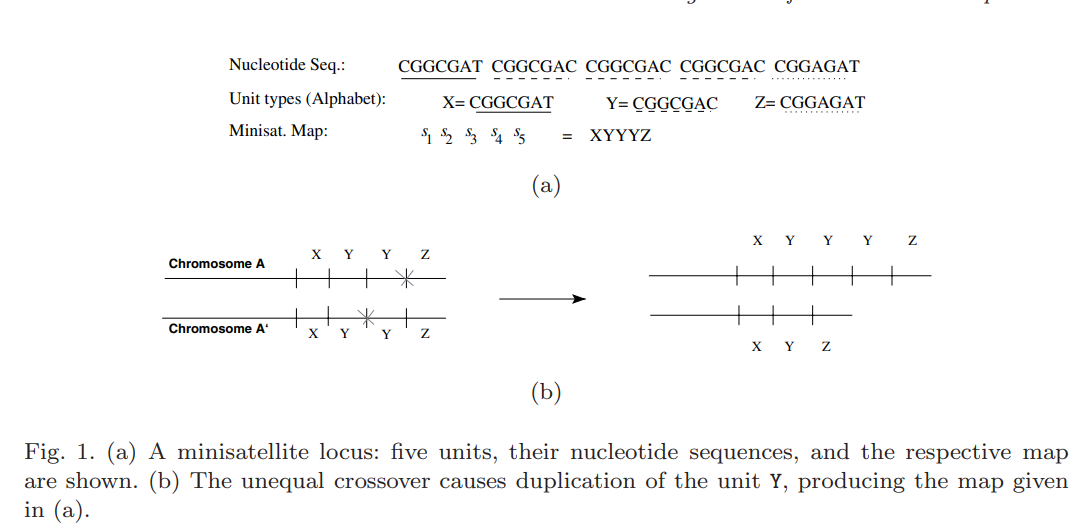
Alignment of minisatellite maps based on run-length encoding scheme
Subsequent duplication events are responsible for the evolution of the minisatellite maps. Alignment of two minisatellite maps should therefore take these duplication events into account, in addition to the well-known edit operations. All algorithms for computing an optimal alignment of two maps, including the one presented here, first deduce the costs of optimal duplication scenarios for all substrings of the given maps. Then, they incorporate the pre-computed costs in the alignment recurrence. However, all previous algorithms addressing this problem are dependent on the number of distinct
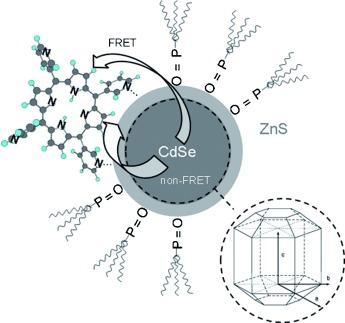
Formation principles and ligand dynamics of nanoassemblies of CdSe quantum dots and functionalised dye molecules
Functional dye molecules, such as porphyrins, attached to CdSe quantum dots (QDs) through anchoring meso-pyridyl substituents, form quasi-stable nanoassemblies. This fact results in photoluminescence (PL) quenching of the QDs both due to Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and the formation of non-radiative surface states under conditions of quantum confinement (non-FRET). The formation process is in competition with the ligand dynamics. At least two timescales are found for the formation of the assemblies: 1) one faster than 60 s attributed to saturation of empty attachment sites and 2)
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 60
- Next page ››
