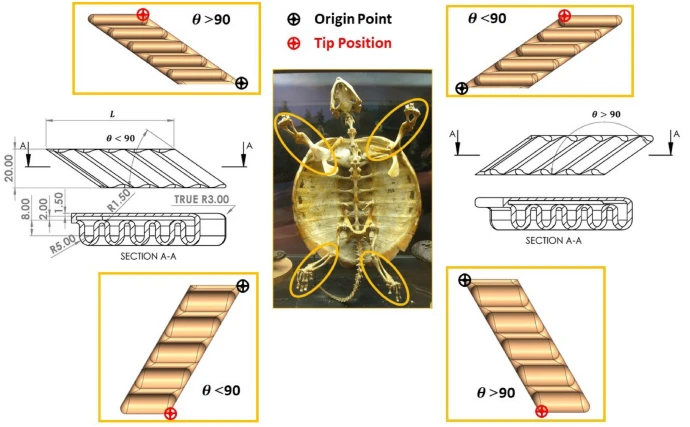
Modelling and implementation of soft bio-mimetic turtle using echo state network and soft pneumatic actuators
Advances of soft robotics enabled better mimicking of biological creatures and closer realization of animals’ motion in the robotics field. The biological creature’s movement has morphology and flexibility that is problematic deportation to a bio-inspired robot. This paper aims to study the ability to mimic turtle motion using a soft pneumatic actuator (SPA) as a turtle flipper limb. SPA’s behavior is simulated using finite element analysis to design turtle flipper at 22 different geometrical configurations, and the simulations are conducted on a large pressure range (0.11–0.4 Mpa). The

Modeling of Nonlinear Enhanced Air Levitation System using NARX Neural Networks
the proposed paper aims to design and model an air levitation system, which is a highly nonlinear system because of its fast dynamics and low damping. The system is trained using a Nonlinear Autoregressive model with exogenous input (NARX model). An enhanced height measurement system, modified setup, and several training techniques have been used to overcome the restrictions that the non-linearity of the system imposes in the literature. The system mathematical model has been illustrated, followed by an identified model using NARX model trained on several input-output data from the physical
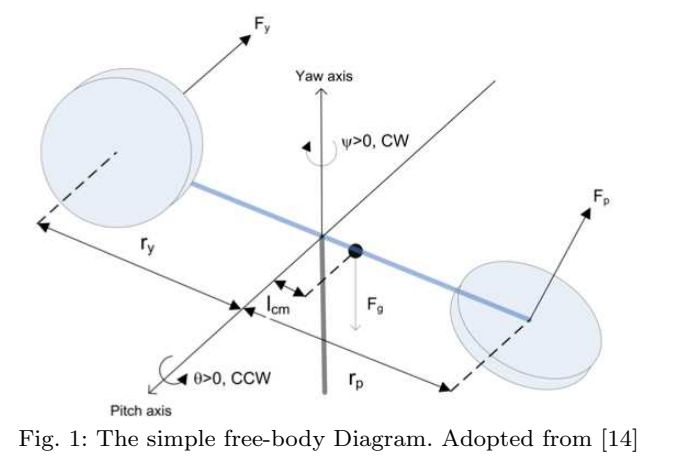
PID Controller for 2-DOFs Twin Rotor MIMO System Tuned with Particle Swarm Optimization
This paper presents the modelling and control of a 2-DOFs Twin rotor multi input multi output (MIMO) system which is a laboratory setup resembling the dynamics of a helicopter. In this paper, the system modelling process is done using the common conventional mathematical model based on Euler-Lagrange method. The transfer functions of the model are used in the different tuning methods to reach the optimal PID gain values. The study uses conventional Proportional-Integral (PI) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers to obtain a robust controller for the system. Particle Swarm
Optimal Design of PID Controller for 2-DOF Drawing Robot Using Bat-Inspired Algorithm
Tuning process which is used to find the optimum values of the proportional integral derivative (PID) parameters, can be performed automatically using meta-heuristics algorithms such as BA (Bat Algorithm), PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization) and ABC (Artificial Bee Colony). This paper presented a theoretical and practical implementation of a drawing robot using BA to tune the PID controller governing the robotic arm which is a non linear system difficult to be controlled using classical control. In line with the above and in order to achieve this aim and meet high performance feedback and robust
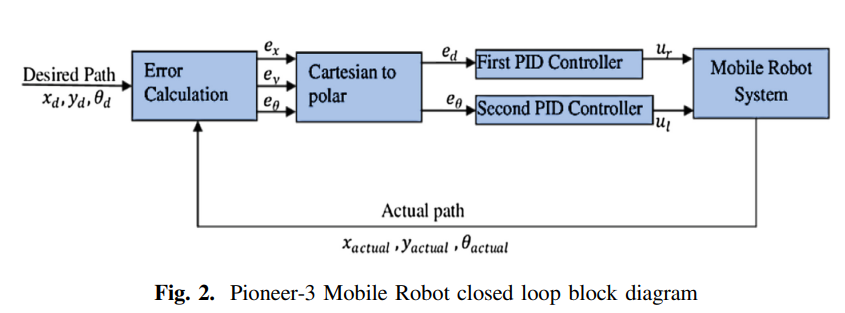
Robust Path Tracking of Mobile Robot Using Fractional Order PID Controller
This paper represents the control of the Pioneer-3 Mobile Robot as a complex non-linear system which provides an object for research nonlinear system kinematics and dynamics analysis. In this paper, the system modeling and simulation is divided into two main parts. The first part is the modeling and simulation using MATLAB and the second part is the whole mechanical design and its characteristics as a function of the motor speed and the torque depending on the system using Virtual Robot Environment Program (V-REP). The study uses Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) and Fractional Order PID
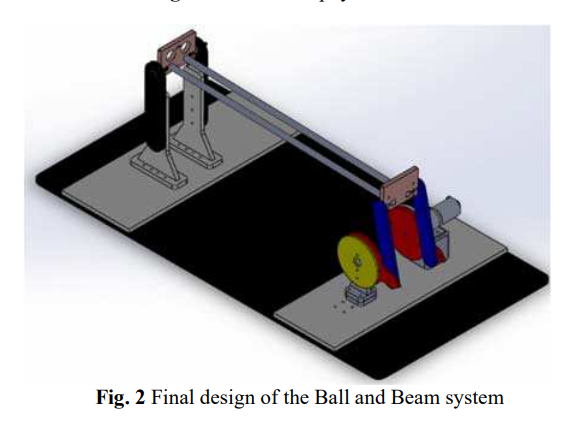
Design and Implementation of a Ball and Beam PID Control System Based on Metaheuristic Techniques
The paper introduces a comparative analysis between three meta-heuristic techniques in the optimization of Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller for a cascaded control of a ball and beam system. The meta-heuristic techniques presented in this study are Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) and Bat Algorithm Optimization (BAO). The model uses a DC motor with encoder to move the beam and a camera as a feedback for the ball position on the beam. The control theory of the system depends on two loops; the first (inner) loop is the DC motor for position control
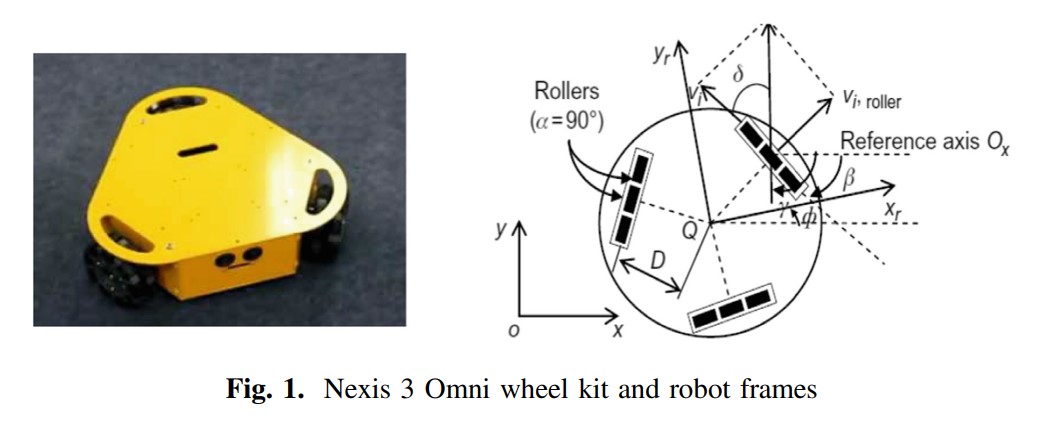
Path Planning Control for 3-Omni Fighting Robot Using PID and Fuzzy Logic Controller
This paper addresses a comparison between some control methods of three Omni wheels firefighting robot due to the variety of maneuverability. To achieve path planning for firefighting robot to reach a specific point with the shortest path, a kinematics model of omni wheel robot is applied with some control algorithms based on PID controller, Fuzzy logic controller and self-tuned PID using fuzzy logic techniques. Hardware prototype has been tested to validate the simulation results. © 2020, Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Implementation and analysis of tunable fractional-order band-pass filter of order 2α
This paper proposes a new design of a 2α-order fractional-order band-pass filter with tunability feature. The proposed filter is approximated with the Continued Fraction Expansion and Matsuda second-order approximations. The realized filter transfer function is based on the Inverse Follow the Leader Feedback configuration, with Operational Transconductance Amplifiers as active elements. As a result, the order of the proposed filter can be adjusted by changing a single parameter, which is the bias current Ibias. A comparison with the previous works is performed, showing the advantage of the
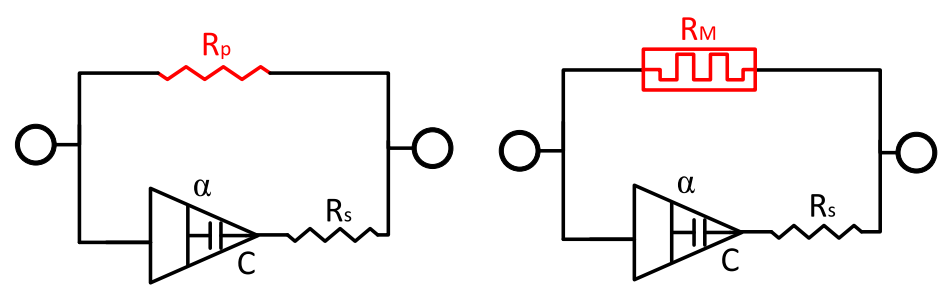
Memristive Bio-Impedance Modeling of Fruits and Vegetables
Recent works show that the plants can exhibit nonlinear memristive behavior when excited with low-frequency signals. However, in the literature, only linear bio-impedance models are extensively considered to model the electrical properties of biological tissues without acknowledging the nonlinear behavior. In this paper, we show with experiments, for the first time, the pinched hysteresis behavior in seven fruits and vegetables including tomato, orange, lemon, aubergine, and kiwi which exhibit single pinch-off point, and others such as carrot and cucumber exhibit double pinch-off points (i.e
Integration of a 2-D periodic nanopattern into thin-film polycrystalline silicon solar cells by nanoimprint lithography
The integration of 2-D periodic nanopattern defined by nanoimprint lithography and dry etching into aluminum-induced crystallization-based polycrystalline silicon thin-film solar cells is investigated experimentally. Compared with the unpatterned cell, an increase of 6% in the light absorption has been achieved thanks to the nanopattern, which, in turn, increased the short-circuit current from 20.6 to 23.8 mA/cm2. The efficiency, on the other hand, has limitedly increased from 6.4% to 6.7%. We show using the transfer length method that the surface topography modification caused by the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 51
- Next page ››
