Fractional-order edge detection masks for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis as a case study
Edge detection is one of the main steps in the image processing field, especially in bio-medical imaging, to diagnose a disease or trace its progress. The transfer of medical images makes them more susceptible to quality degradation due to any imposed noise. Hence, the protection of this data against noise is a persistent need. The efficiency of fractional-order filters to detect fine details and their high noise robustness, unlike the integer-order filters, it renders them an attractive solution for biomedical edge detection. In this work, two novel central fractional-order masks are proposed
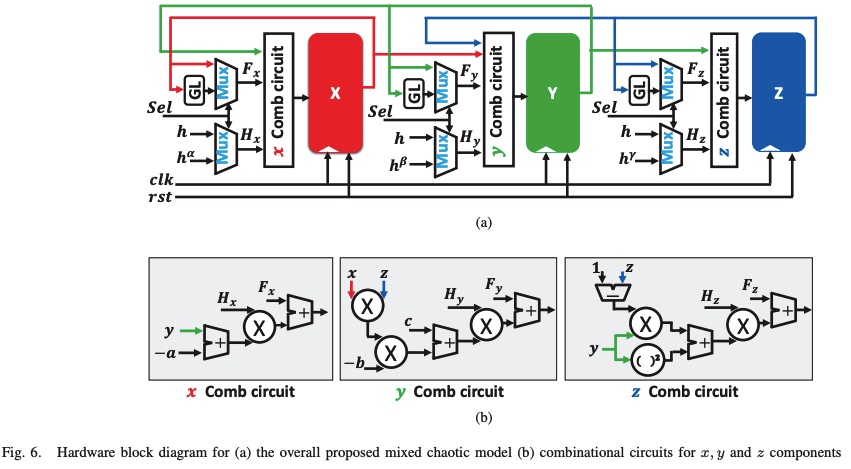
A Digital Hardware Implementation for A new Mixed-Order Nonlinear 3-D Chaotic System
This paper introduces a generic modeling for a 3-D nonlinear chaotic based on fractional-order mathematical rules. Also, a novel modeling for the system using a mixture between integer and fractional-order calculus is proposed. Dynamics of the new realization are illustrated using phase portrait diagrams with complex behavior. Also, a great change in the parameter ranges is investigated using bifurcation diagrams. MATLAB and Xilinx ISE 14.5 are used in system simulations. Furthermore, the digital hardware implementation is done using Xilinx FPGA Virtex-5 kit. The synthesis report shows that
FPGA Realizations of Chaotic Epidemic and Disease Models including Covid-19
The spread of epidemics and diseases is known to exhibit chaotic dynamics; a fact confirmed by many developed mathematical models. However, to the best of our knowledge, no attempt to realize any of these chaotic models in analog or digital electronic form has been reported in the literature. In this work, we report on the efficient FPGA implementations of three different virus spreading models and one disease progress model. In particular, the Ebola, Influenza, and COVID-19 virus spreading models in addition to a Cancer disease progress model are first numerically analyzed for parameter
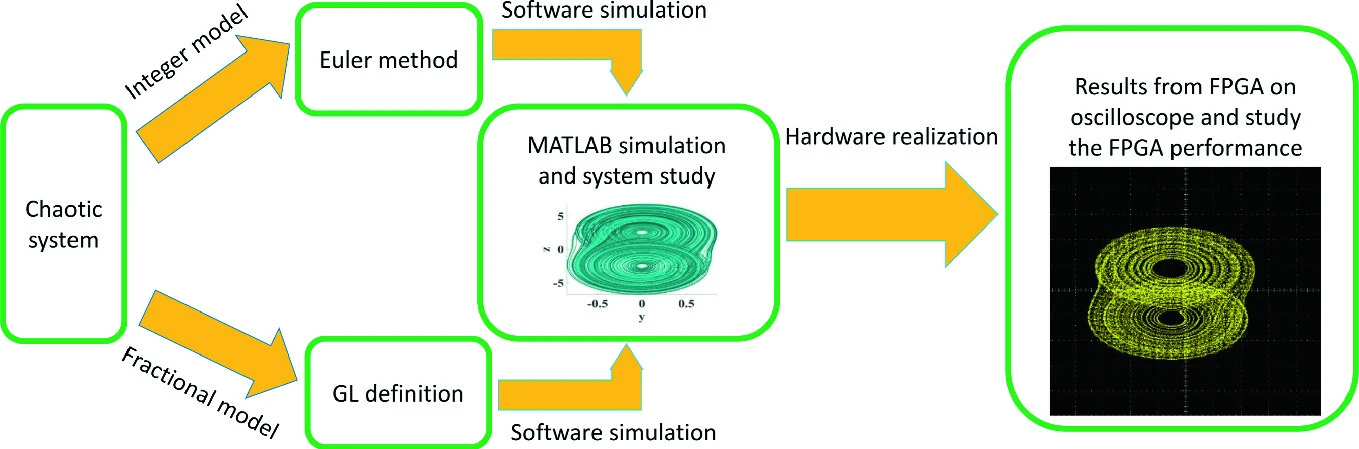
Reconfigurable FPGA Realization of Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems
This paper proposes FPGA realization of an IP core for generic fractional-order derivative based on Grünwald-Letnikov approximation. This generic design is applied to achieve reconfigurable realization of fractional-order chaotic systems. The fractional-order real-time configuration boosts the suitability of this particular realization for different applications, including dynamic switching, synchronization, and encryption. The proposed design targets optimized utilization of the FPGA internal resources and efficient employment of the external peripherals: switches and I/O ports in the FPGA
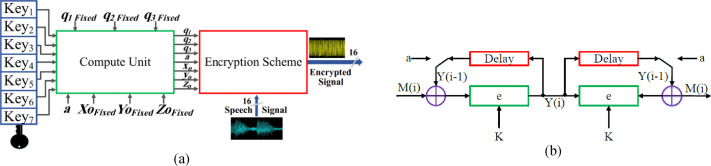
FPGA implementation of sound encryption system based on fractional-order chaotic systems
This paper introduces design and FPGA implementation of sound encryption system based on a fractional-order chaotic system. Also, it presents the FPGA implementation of Tang, Yalcin, and Özoǧuz fractional order chaotic systems. The Grunwald-Letnikov (GL) definition is used to generalize the investigated systems into the fractional-order domain. Also, the variation of parameters for each system is investigated against the window size of the GL definition. Xilinx ISE 14.5 is used to simulate the proposed design. Also, some hardware reduction techniques are applied to decrease hardware
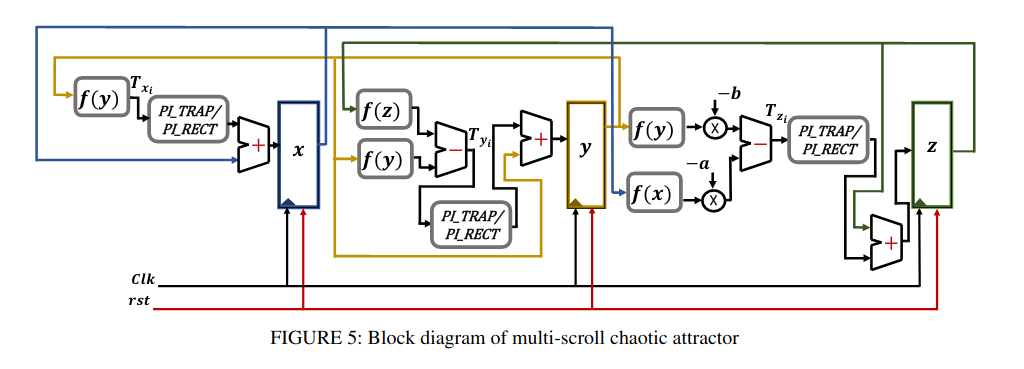
Numerical Simulations and FPGA Implementations of Fractional-Order Systems Based on Product Integration Rules
Product integration (PI) rules are well known numerical techniques that are used to solve differential equations of integer and, recently, fractional orders. Due to the high memory dependency of the PI rules used in solving fractional-order systems (FOS), their hardware implementation is very difficult and resources-demanding. In this paper, modified versions of the PI rules are introduced to facilitate their digital implementations. The studied rules are PI rectangular, PI trapezoidal, and predict-evaluate-correct-evaluate (PECE) rules. The three modified versions of the PI rules are
FPGA implementation of integer/fractional chaotic systems
Chaotic systems have remarkable importance in capturing some complex features of the physical process. Recently, fractional calculus becomes a vigorous tool in characterizing the dynamics of complex systems. The fractional-order chaotic systems increase the chaotic behavior in new dimensions and add extra degrees of freedom, which increase system controllability. In this chapter, FPGA implementation of different integer and fractional-order chaotic systems is presented. The investigated integer-order systems include Chua double scroll chaotic system and the modified Chua N-scroll chaotic
CNTFET design of a multiple-port ternary register file
Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. Such advantage motivated the development of ternary processing units especially with CNTFET which offers better power and delay results compared to CMOS-based realization. In this paper, we propose a variety of circuit realizations for the ternary memory elements that are needed in any processor including ternary D-latch, and ternary D-flip-flop. These basic building blocks are then used to design a ternary register file with multiple read and write ports. This paper is
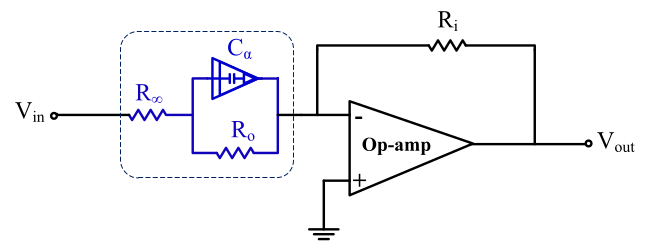
A Modified Differentiator Circuit for Extracting Cole-Impedance Model Parameters Using Meta-heuristic Optimization Algorithms
A differentiator-based set up is proposed as an alternative solution to measure bio-impedance. The method is modifying the differentiator circuit, replacing the capacitor with the Cole-impedance model representing the biological (fruit) sample. The proposed differentiator gain response (with the embedded fruit) is experimentally recorded. The experimental data’s post-processing is performed using meta-heuristic optimization techniques to extract the Cole-impedance model unknown parameters by solving a group of nonlinear equations. Three meta-heuristic optimization algorithms are used: the moth
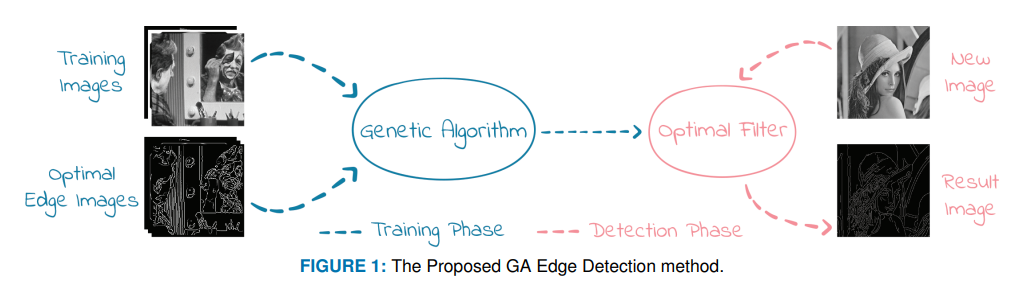
Optimized Edge Detection Technique for Brain Tumor Detection in MR Images
Genetic algorithms (GAs) are intended to look for the optimum solution by eliminating the gene strings with the worst fitness. Hence, this paper proposes an optimized edge detection technique based on a genetic algorithm. A training dataset that consists of simple images and their corresponding optimal edge features is employed to obtain the optimum filter coefficients along with the optimum thresholding algorithm. Qualitative and quantitative performance analyses are investigated based on several well-known metrics. The performance of the proposed genetic algorithm-based cost minimization
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 49
- Next page ››
