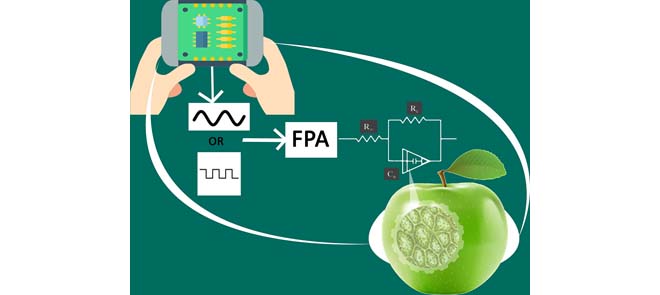
Extracting Optimized Bio-Impedance Model Parameters Using Different Topologies of Oscillators
This paper demonstrates the possibility of extracting the single-dispersion and double-dispersion Cole-bio-impedance model parameters using oscillators (sinusoidal or relaxation). The method is based on replacing selected components in the oscillator structure with the biological sample under test and then using the Flower Pollination optimization Algorithm (FPA) to solve a set of nonlinear equations in order to extract the unknown model parameters. Minimum component sinusoidal oscillators and relaxation oscillators are used in this work and experimental results on three samples of four
Cole bio-impedance model variations in daucus carota sativus under heating and freezing conditions
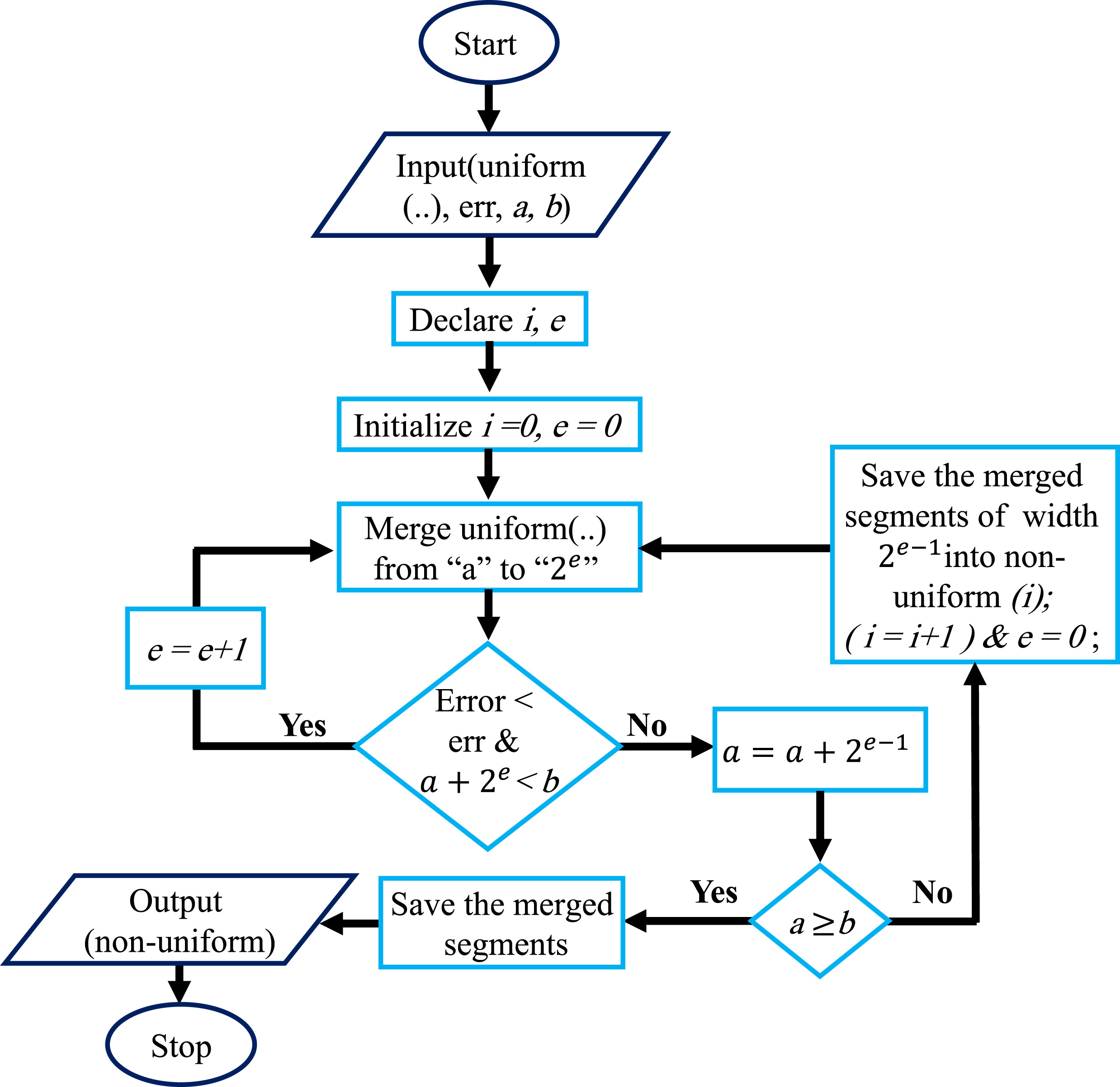
This paper reports on the variations in the parameters of the single dispersion Cole bio-impedance model of Daucus Carota Sativus (carrots) under heating and freezing conditions. Experiments are conducted on six samples with recorded live bio-impedance spectra versus temperature. The Cole model parameters are extracted from the measured data using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA) optimization technique and their variations are correlated with well-known bio-chemical and bio-mechanical variations. This represents a non-invasive method for characterizing and measuring the degree of change
Hardware realization of a secure and enhanced s-box based speech encryption engine
This paper presents a secure and efficient substitution box (s-box) for speech encryption applications. The proposed s-box data changes every clock cycle to swap the input signal with different data, where it generated based on a new algorithm and a memristor chaotic system. Bifurcation diagrams for all memristor chaotic system parameters are introduced to stand for the chaotic range of each parameter. Moreover, the effect of each component inside the proposed encryption system is studied, and the security of the system is validated through perceptual and statistical tests. The size of the
Ternary Functions Design Using Memristive Threshold Logic
Memristive threshold logic (MTL) concept is emerged in many circuits to enable high-performance systems in terms of power, energy, area, and delay. This paper proposes a systematic method for building two-bit ternary number functions based on the MTL concept. The proposed method is applied to build the basic ternary arithmetic operations. The implementation of two-bit adder and multiplier is presented in the unbalanced ternary number representation. The proposed designs are verified by using VTEAM memristor and Stanford CNTFET transistor models. Finally, a comparison between the proposed
Synchronization and FPGA realization of fractional-order Izhikevich neuron model
This paper generalizes the Izhikevich neuron model in the fractional-order domain for better modeling of neuron dynamics. Accurate and computationally efficient numerical techniques such as non-standard finite difference (NSFD) scheme is used to solve the neuron system in the fractional-order domain for different cases. Neuron synchronization plays an important role in the process of information exchange among coupled neurons. The general formula for the synchronization of different Izhikevich neurons is proposed. Also, the synchronization of two and three neurons are studied at different
Two implementations of fractional-order relaxation oscillators
This work proposes general formulas for designing two different topologies of fractional-order relaxation oscillators. One topology contains an Operational Amplifier and the other one relies on an Operational Trans-Resistance Amplifier. The design procedure hinges on the general fractional-order natural and step responses of RC, which is proved in this work depending on Mittag Leffler function. The proposed topologies can be controlled to generate symmetrical and non-symmetrical square wave signals. They also benefit from the employment of fractional-order capacitors (FOCs), which makes it
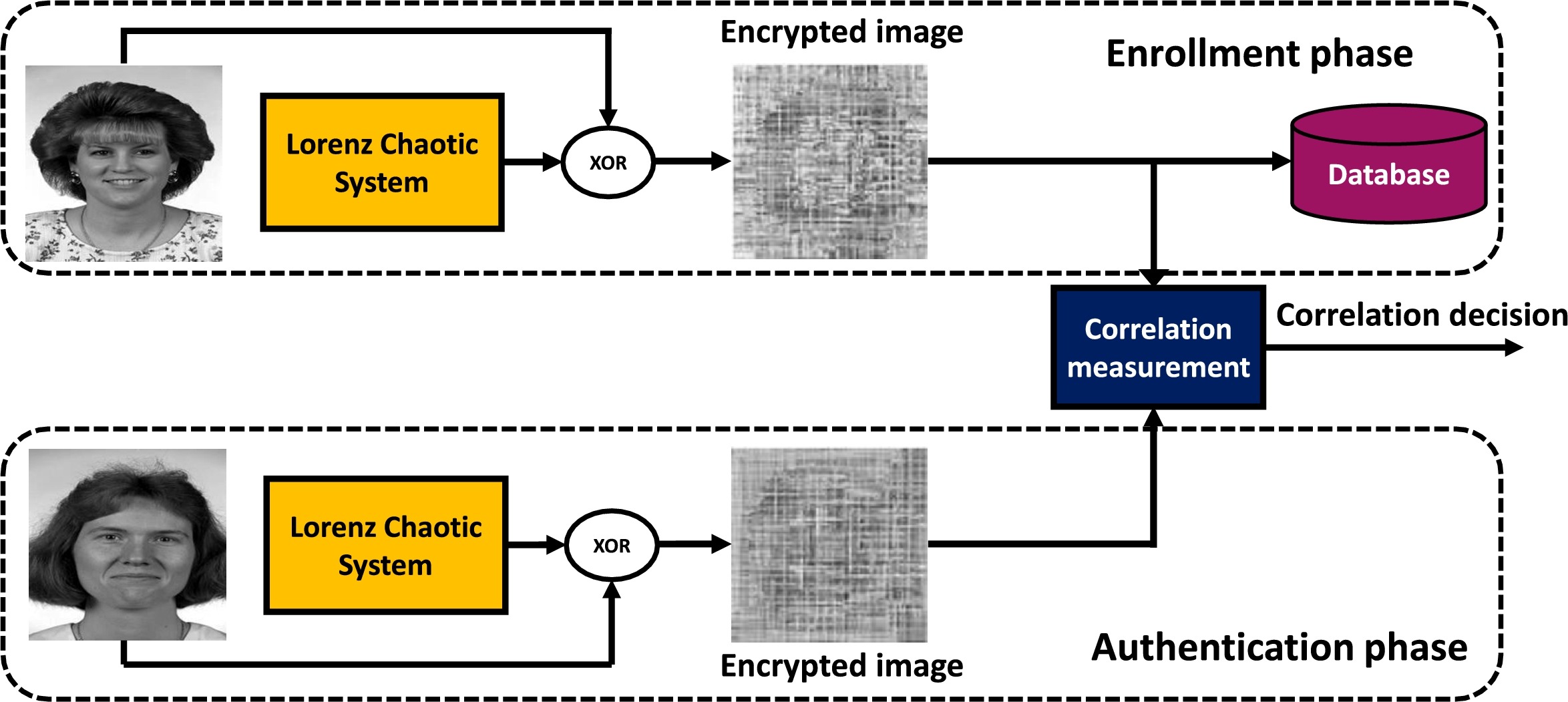
Cancellable face recognition based on fractional-order Lorenz chaotic system and Haar wavelet fusion
Cancellable biometrics is the art of generating distorted or encrypted templates of original biometric templates. The evolution of cancellable biometrics is attributed to the advanced hacking technologies that can capture the original stored biometrics from databases. One of the solutions for this problem is to store cancellable biometric templates in the database rather than the original ones. This paper presents a cancellable face recognition scheme that is based on face image encryption with Fractional-Order (FO) Lorenz chaotic system. The basic idea is to generate user-specific random keys
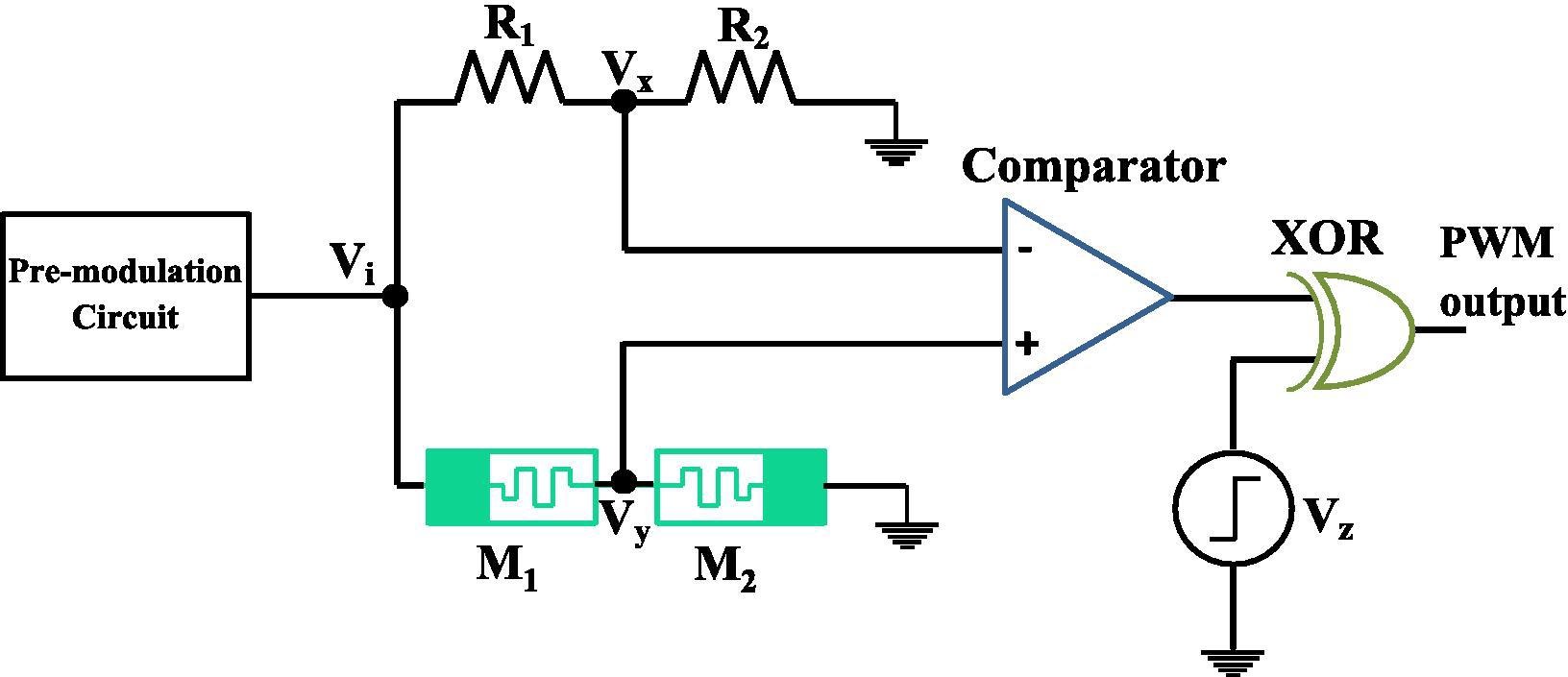
Center pulse width modulation implementation based on memristor
This paper introduces two new versions for memristor-based center pulse-width modulator (PWM) circuits. The proposed circuits use only one comparator which reduces the circuit complexity and power dissipation compared to a former work. The first design is based on two memristors and two resistors while the second design is based on four memristors. Theoretical analysis is provided, and the numerical solution is handled on MATLAB. Simulation is carried out on Cadence software, and the results follow the theoretical analysis. The experiment is implemented using commercial off-the-shelf
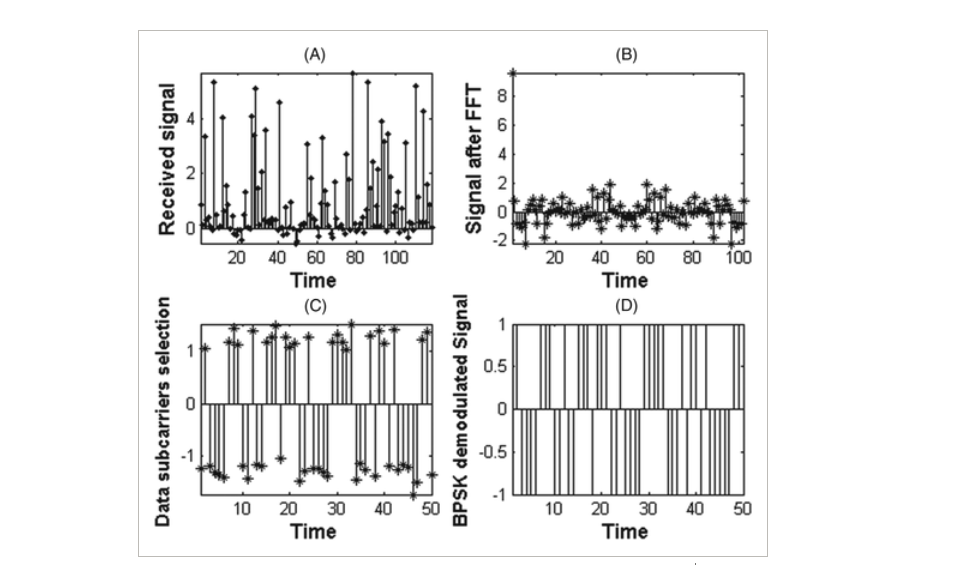
Odd clipping optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing for VLC system
The Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) has emerged as one of the promising techniques because of its robustness to multipath fading with high-speed data transmission. Classical bipolar OFDM cannot be used in intensity modulated with direct detection (IM/DD) optical communication systems, as visible light communication (VLC), so many optical modulation techniques as asymmetrical clipped optical OFDM (ACO-OFDM) and DC-Clipped OFDM (DCO-OFDM) have been investigated. In this paper, we introduce a novel optical modulation scheme that meets the optical communications requirements. The
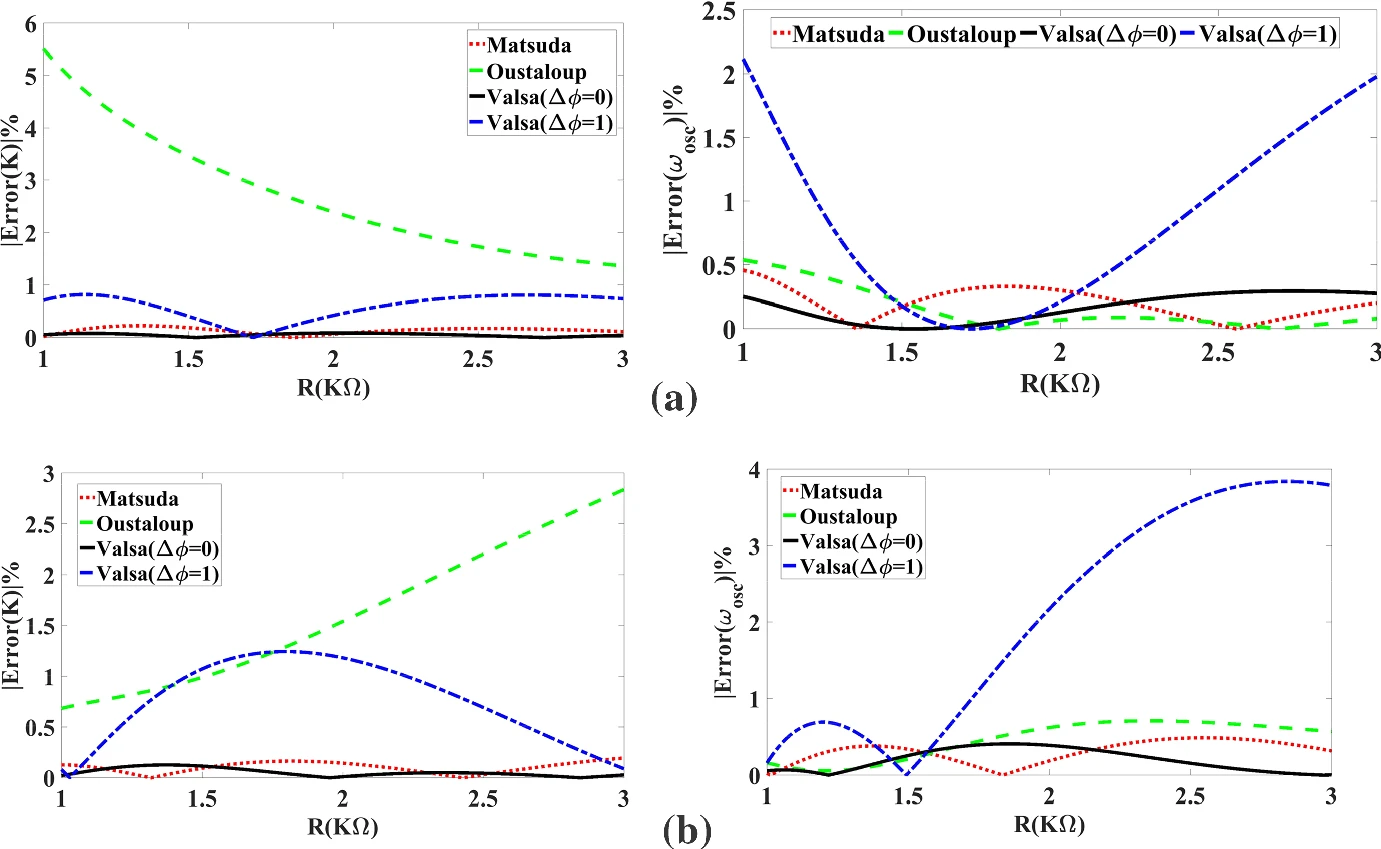
All Possible Topologies of the Fractional-Order Wien Oscillator Family Using Different Approximation Techniques
This paper introduces all the possible topologies of the Wien bridge oscillator family. This family has 72 topologies, 24 of them contain only RC or RL pairs, and the rest contain mixed pairs. The complete mathematical analysis of all twelve possible capacitive-based topologies is proposed in the fractional-order domain. The investigated circuits can be categorized into two groups, each with a similar characteristic equation. Three integer-order approximation techniques for the Laplacian operator sα are employed to solve and simulate the Wien bridge system. The studied approximations are those
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 47
- Next page ››
