Controlled alternate quantum walks based privacy preserving healthcare images in Internet of Things
The development of quantum computers and quantum algorithms conveys a challenging scenario for several cryptographic protocols due to the mathematical scaffolding upon which those protocols have been built. Quantum walks constitute a universal quantum computational model which is widely used in various fields, including quantum algorithms and cryptography. Quantum walks can be utilized as a powerful tool for the development of modern chaos-based cryptographic applications due to their nonlinear dynamical behavior and high sensitivity to initial conditions. In this paper, we propose new
Features selection for building an early diagnosis machine learning model for Parkinson's disease
In this work, different approaches were evaluated to optimize building machine learning classification models for the early diagnosis of the Parkinson disease. The goal was to sort the medical measurements and select the most relevant parameters to build a faster and more accurate model using feature selection techniques. Decreasing the number of features to build a model could lead to more efficient machine learning algorithm and help doctors to focus on what are the most important measurements to take into account. For feature selection we compared the Filter and Wrapper techniques. Then we
An approach for extracting and disambiguating arabic persons' names using clustered dictionaries and scored patterns
Building a system to extract Arabic named entities is a complex task due to the ambiguity and structure of Arabic text. Previous approaches that have tackled the problem of Arabic named entity recognition relied heavily on Arabic parsers and taggers combined with a huge set of gazetteers and sometimes large training sets to solve the ambiguity problem. But while these approaches are applicable to modern standard Arabic (MSA) text, they cannot handle colloquial Arabic. With the rapid increase in online social media usage by Arabic speakers, it is important to build an Arabic named entity
Transform domain two dimensional and diagonal modular principal component analysis for facial recognition employing different windowing techniques
Spatial domain facial recognition Modular IMage Principal Component Analysis (MIMPCA) has an improved recognition rate compared to the conventional PCA. In the MPCA, face images are divided into smaller sub-images and the PCA approach is applied to each of these sub-images. In this work, the Transform Domain implementation of MPCA is presented. The facial image has two representations. The Two Dimensional MPCA (TD-2D-MPCA) and the Diagonal matrix MPCA (TD-Dia-MPCA). The sub-images are processed using both non-overlapping and overlapping windows. All the test results, for noise free and noisy
Towards Efficient Online Topic Detection through Automated Bursty Feature Detection from Arabic Twitter Streams
Detecting trending topics or events from Twitter is an active research area. The first step in detecting such topics focuses on efficiently capturing textual features that exhibit an unusual high rate of appearance during a specific timeframe. Previous work in this area has resulted in coining the term "detecting bursty features" to refer to this step. In this paper, TFIDF, entropy, and stream chunking are adapted to investigate a new technique for detecting bursty features from an Arabic Twitter stream. Experimental results comparing bursty features extracted from Twitter streams, to Twitter
Survey and taxonomy of information-centric vehicular networking security attacks
Information Centric Networks (ICNs) overcome the current IP-based networks weakness and aim to ensure efficient data distribution. The Main ICN features are location-independent naming, in-network caching, name-based routing, built-in security, and high mobility. ICN vehicular networks stratify the ICN architecture on the Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) to reinforce a massive amount of data transmission and handle the critical time interests inside the vehicular networks while taking into consideration the vehicles’ high mobility. Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) gather the real-time
Improved estimation of the cardiac global function using combined long and short axis MRI images of the heart
Background: Estimating the left ventricular (LV) volumes at the different cardiac phases is necessary for evaluating the cardiac global function. In cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, accurate estimation of the LV volumes requires the processing a relatively large number of parallel short-axis cross-sectional images of the LV (typically from 9 to 12). Nevertheless, it is inevitable sometimes to estimate the volume from a small number of cross-sectional images, which can lead to a significant reduction of the volume estimation accuracy. This usually encountered when a number of cross-sectional
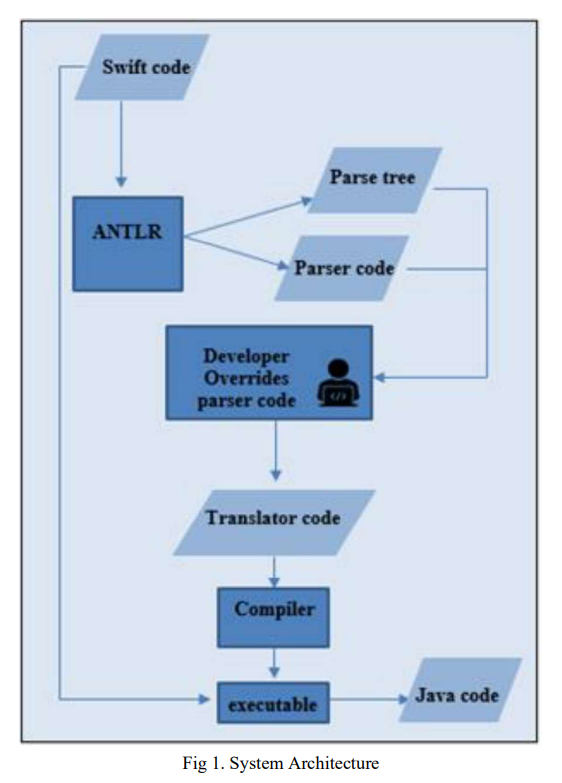
Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications code converter: Swift to java
Numerous commercial tools like Xamarin, React Native and PhoneGap utilize the concept of cross-platform mobile applications development that builds applications once and runs it everywhere opposed to native mobile app development that writes in a specific programming language for every platform. These commercial tools are not very efficient for native developers as mobile applications must be written in specific language and they need the usage of specific frameworks. In this paper, a suggested approach in TCAIOSC tool to convert mobile applications from Android to iOS is used to develop the
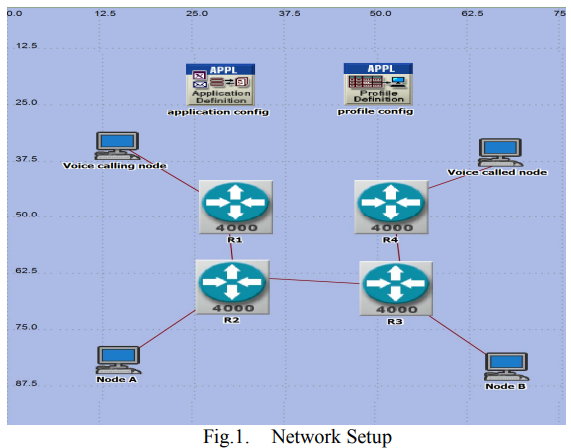
VoIP performance evaluation over IPv4-6 and manually configured tunnels
IPv4 address space is exhausted. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) developed IPv6 -the upgrade of IPv4- to satisfy the continual increase of the IP address needs. The Internet is so ramified and enormous that the complete transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is slow. Therefore, their coexistence is inevitable. Manually configured tunnels are an important solution to allow this co-existence that allows transmitting native IPv6 packets over IPv4 networks. Meanwhile, VoIP is also gaining momentum with expectation to occupy considerable percentage of Internet traffic. In this paper, we compare the
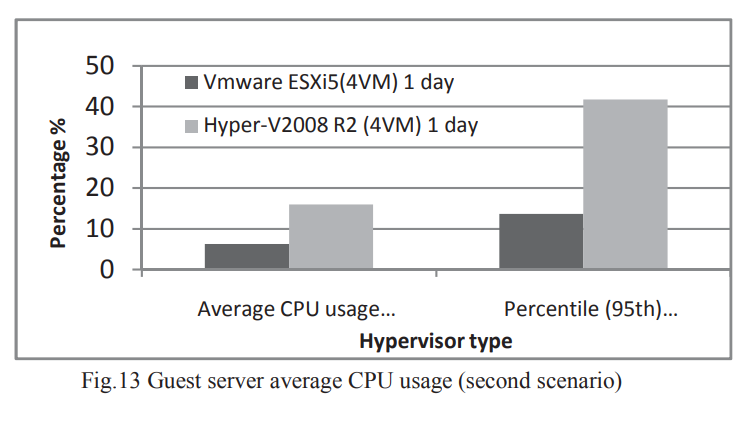
Performance evaluation and comparison of the top market virtualization hypervisors
The virtualization of IT infrastructure enables the consolidation and pooling of IT resources so that they can be shared over diverse applications to offset the limitation of shrinking resources and growing business needs. It provides a logical abstraction of physical computing resources and creates computing environments that are not restricted by physical configuration or implementation. Virtualization is very important for cloud computing because the delivery of services is simplified by providing a platform for optimizing complex IT resources in a scalable manner, which makes cloud
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 25
- Next page ››
