Lid-Driven Cavity Flow with Elliptic Obstacle at Different Orientations
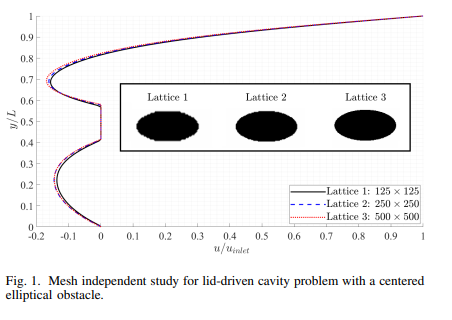
The aim of the present work is to predict the flow field around an elliptic obstacle at different orientations inside a square Lid-Driven Cavity (LDC). The Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) is used to simulate the flow at a Reynolds number, Re, of 100, using the two-dimensional nine-velocity, (D2Q9) lattice configuration and the BGK collision operator. The in-house code is validated using data from the literature for the case of LDC with a central circular cylinder. Different ellipse orientations are tested (0°, 30°, 45°, 90°, 120°, 145°, and 150°) to check the effect of orientation on the vortex formation. Further, the cases are compared with the case of a circular obstacle. The results show that the orientation affects the induced vortex size and location. The vortex size is maximum at an orientation angle of 0° and starts to decrease until it reaches its minimum size at an orientation angle of 90°. Then, it increases again with the increase of the orientation angle until 180°. © 2021 IEEE.