Breadcrumb
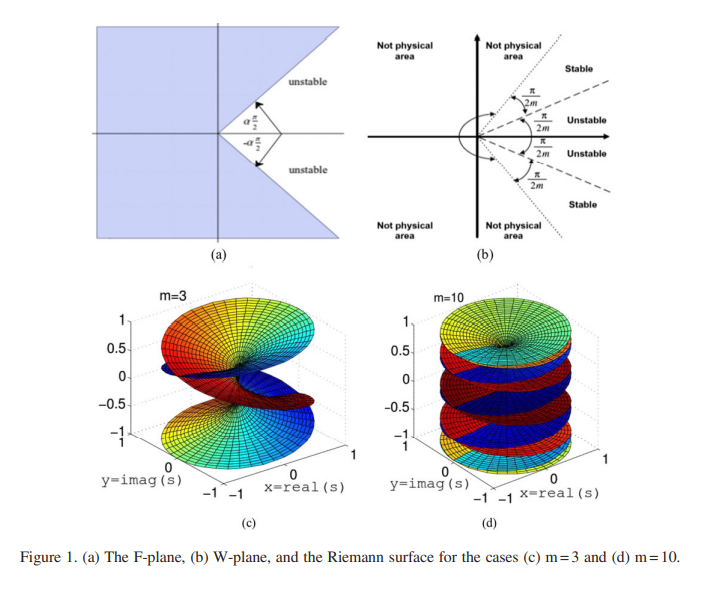
Fundamentals of fractional-order LTI circuits and systems: number of poles, stability, time and frequency responses
This paper investigates some basic concepts of fractional-order linear time invariant systems related to their physical and non-physical transfer functions, poles, stability, time domain, frequency domain, and their relationships for different fractional-order differential equations. The analytical formula that calculates the number of poles in physical and non-physical s-plane for different orders is achieved and verified using many practical examples. The stability contour versus the number of poles in the physical s-plane for different fractional-order systems is discussed in addition to
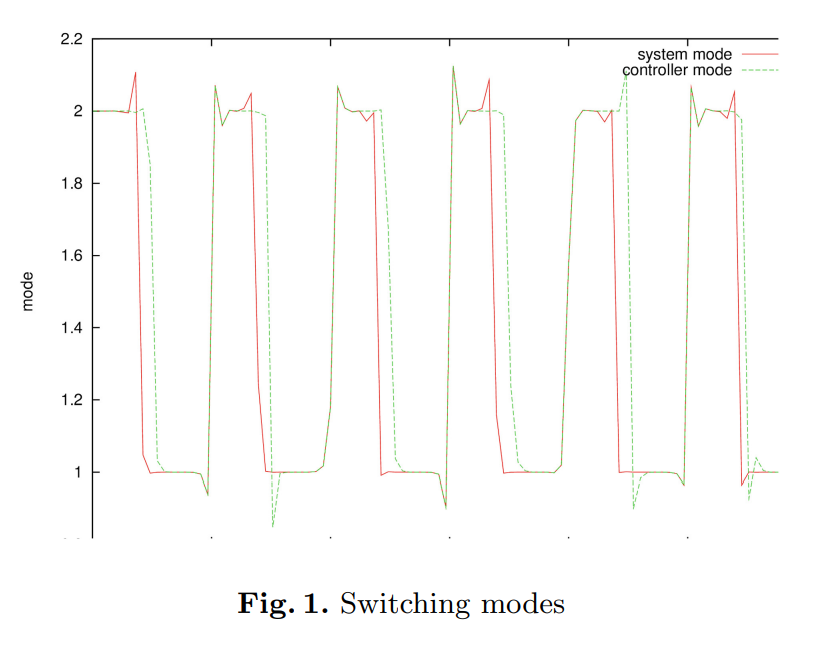
Robust control for asynchronous switched nonlinear systems with time varying delays
In this article a novel robust controller for the control of switched nonlinear systems with asynchronous switching is proposed considering state delays. The proposed approach improves the actual methodologies found in literature in which the disturbance rejection properties of these two methodologies consider a disturbance equal to zero but the proposed robust controller considers any kind of disturbances that makes this strategy to surpass other similar methodologies. The main objective is that the robust controller stabilizes the studied system in matched and unmatched modes considering the

New Trends on Modeling, Design, and Control of Chaotic Systems
[No abstract available]
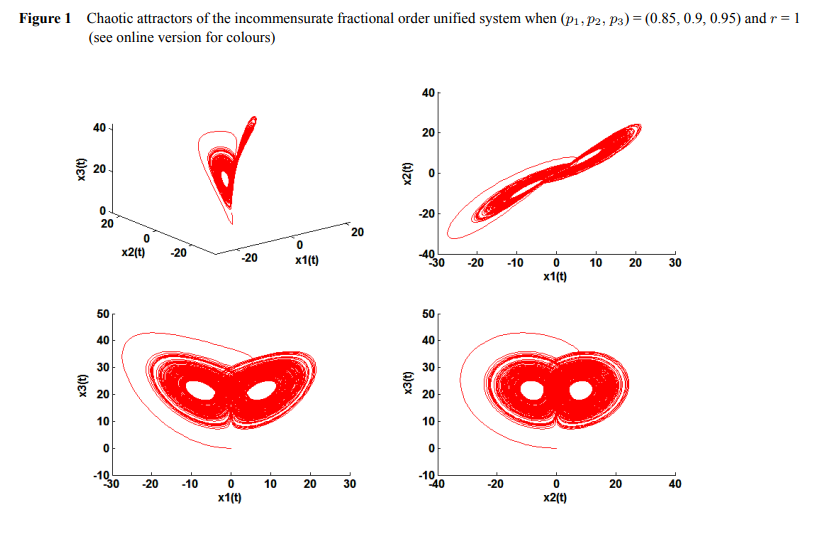
A new fractional hybrid chaos synchronisation
Over the last decades, synchronisation of chaotic systems has become an active research area and has been extensively and intensively studied due to the variety of important applications. Different types of chaos synchronisation have been presented, and many various methods and techniques for chaos synchronisation have been reported to investigate some types of chaos. In this paper, by combining full state hybrid projective synchronisation (FSHPS) and inverse full state hybrid projective synchronisation (IFSHPS), a new type of hybrid synchronisation between different dimensional incommensurate
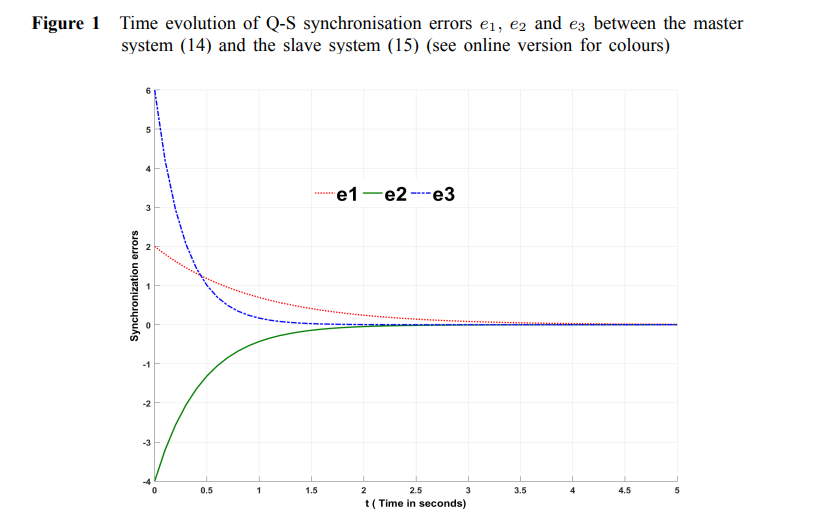
On a simple approach for Q-S synchronisation of chaotic dynamical systems in continuous-time
In this paper, the problem of Q-S synchronisation for arbitrary dimensional chaotic dynamical systems in continuous-time is investigated. Based on nonlinear control method, we would like to present a constructive scheme to study the Q-S synchronisation between n-dimensional master chaotic system and m-dimensional slave chaotic system in arbitrary dimension. The new derived synchronisation result is proved using Lyapunov stability theory. In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, our approach is applied to some typical chaotic systems and numerical simulations are given to
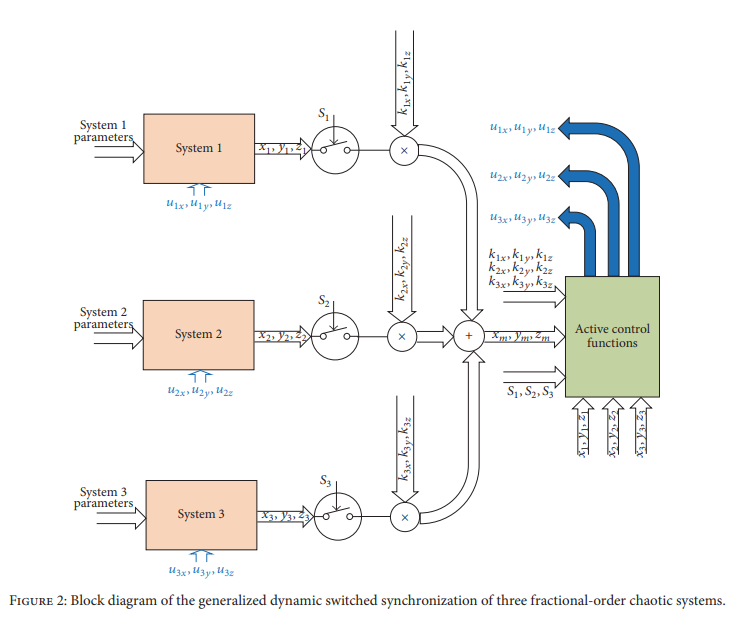
Generalized dynamic switched synchronization between combinations of fractional-order chaotic systems
This paper proposes a novel generalized switched synchronization scheme among n fractional-order chaotic systems with various operatingmodes. Digital dynamic switches and dynamic scaling factors are employed, which offermany new capabilities. Dynamic switches determine the role of each system as a master or a slave. A system can either have a fixed role throughout the simulation time (static switching) or switch its role one or more times (dynamic switching). Dynamic scaling factors are used for each state variable of the master system. Such scaling factors control whether the master is a
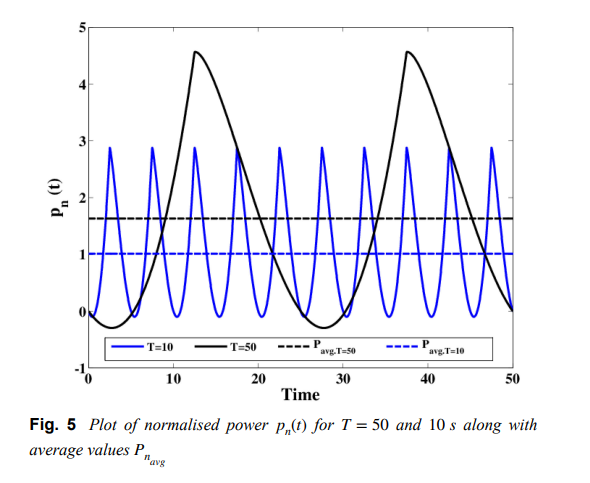
Low-voltage commercial super-capacitor response to periodic linear-with-time current excitation: A case study
The response of a commercial super-capacitor to an applied periodic current excitation in the form of a triangular waveform is investigated in this study. This waveform has a linear-with-time variation which enables linear charging and discharging of the device. A model consisting of a linear resistance Rs and a constant phase element is used to describe the super-capacitor impedance and expressions for the voltage across the device, the power, and stored energy are derived using concepts from fractional calculus. Experimental results are shown and an application of the study to super
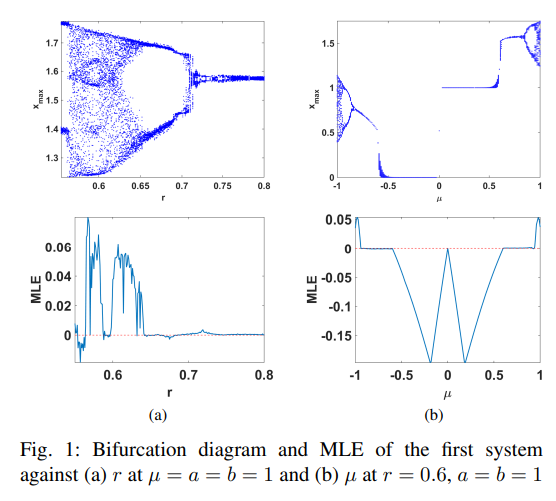
Chaotic systems based on jerk equation and discrete maps with scaling parameters
In the recent decades, applications of chaotic systems have flourished in various fields. Hence, there is an increasing demand on generalized, modified and novel chaotic systems. In this paper, we combine the general equation of jerk-based chaotic systems with simple scaled discrete chaotic maps. Numerical simulations of the properties of two systems, each with four control parameters, are presented. The parameters show interesting behaviors and dependencies among them. In addition, they exhibit controlling capabilities of the ranges of system responses, hence the size of the attractor diagram
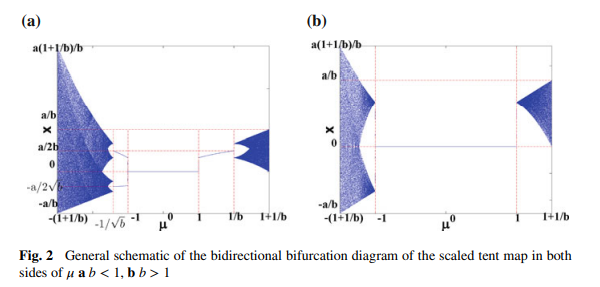
Chaos and bifurcation in controllable jerk-based self-excited attractors
In the recent decades, utilization of chaotic systems has flourished in various engineering applications. Hence, there is an increasing demand on generalized, modified and novel chaotic systems. This chapter combines the general equation of jerk-based chaotic systems with simple scaled discrete chaotic maps. Two continuous chaotic systems based on jerk-equation and discrete maps with scaling parameters are presented. The first system employs the scaled tent map, while the other employs the scaled logistic map. The effects of different parameters on the type of the response of each system are
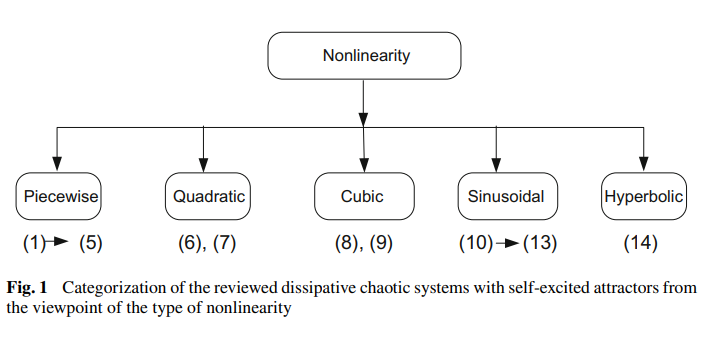
Self-excited attractors in jerk systems: Overview and numerical investigation of chaos production
Chaos theory has attracted the interest of the scientific community because of its broad range of applications, such as in secure communications, cryptography or modeling multi-disciplinary phenomena. Continuous flows, which are expressed in terms of ordinary differential equations, can have numerous types of post transient solutions. Reporting when these systems of differential equations exhibit chaos represents a rich research field. A self-excited chaotic attractor can be detected through a numerical method in which a trajectory starting from a point on the unstable manifold in the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››

