Breadcrumb
Current-Mode Multiplier Accumulator Design using a Memristor-Transistor Crossbar Architecture
This paper discusses the implementation of a Multiplier Accumulator (MAC) design using memristor and crossbar architecture. MAC consists of an array of memristors alongside transistors making a cell that works as a switch (i.e., turned ON or OFF). When a cell is selected, it adds the current in the array path, followed by a current mirror circuit amplified to determine the accumulated current. A traditional MAC is also implemented to compare it with the proposed MAC. The proposed MAC consumed power of 3.9μW, while the traditional MAC consumed power of 19μW. The delay of the proposed MAC is 1
Experimental investigation of innovative active packaging biofilms using electrical impedance spectroscopy
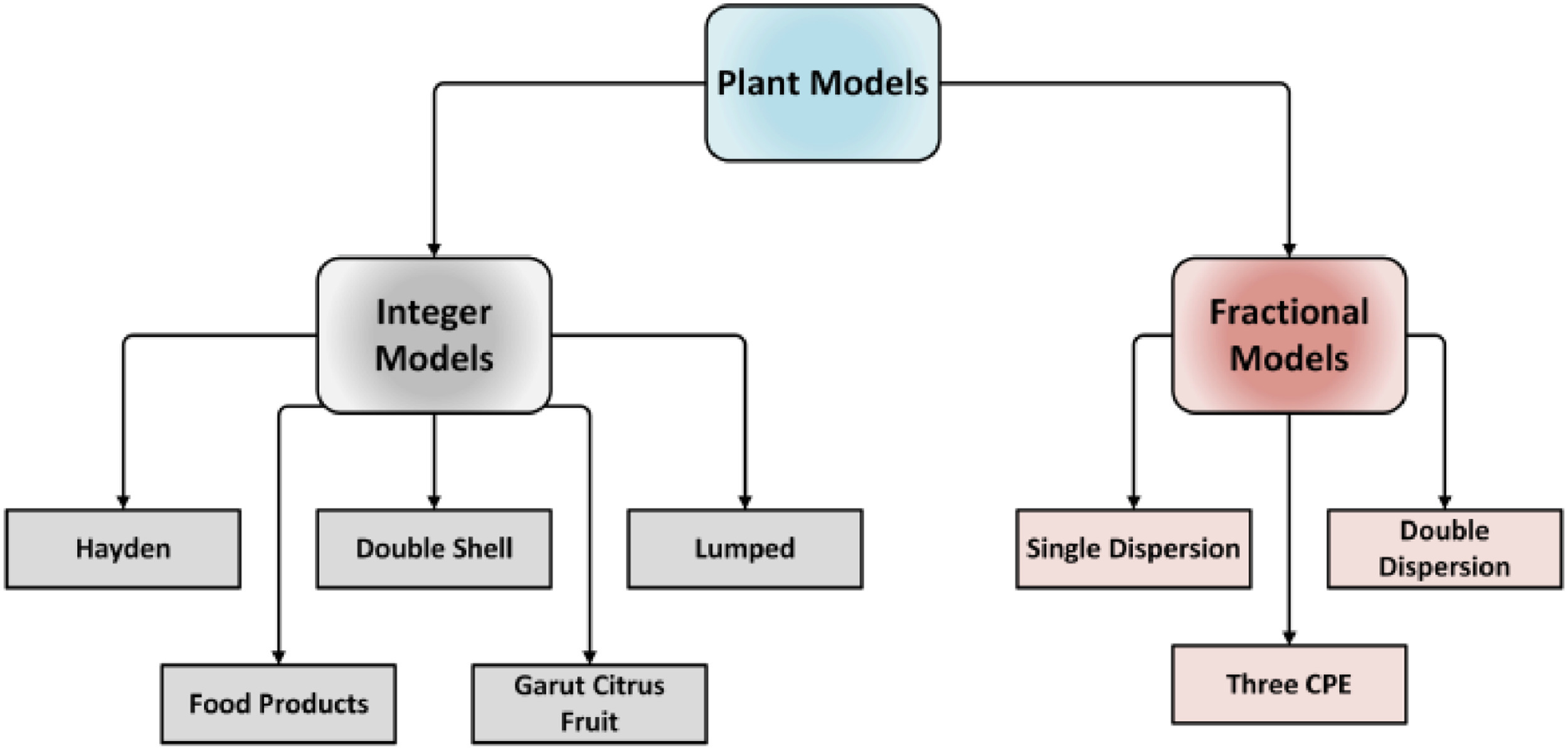
Switched active control synchronization of three fractional order chaotic systems
This paper discusses the continuous effect of fractional order parameter on two chaotic systems. Switched synchronization of three different fractional order chaotic systems is presented as an extension for synchronizing two different systems using active control. The proposed technique, which is based on the switching parameters and the scaling factors that control the choices of master and slave systems, is explained. The NonStandard Finite Difference method is used for the numerical solution of the fractional order master and slave systems. Four cases and many numeric simulations are
Comparison and database development of four recent ASM3 model extensions
In the last decade, many Activated Sludge Model No. 3 (ASM3) extensions were proposed to adopt new concepts such as simultaneous storage and growth of heterotrophic organisms and two-step nitrification-denitrification processes. From these ASM3 model extensions, four are included in this study: ASM3 with two-step nitrification-denitrification, ASM3 for simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic storage-growth, ASM3 extension for two-step nitrification-denitrification, and ASM3 for simultaneous storage-growth and nitrification-denitrification. The four models are analyzed and compared to the
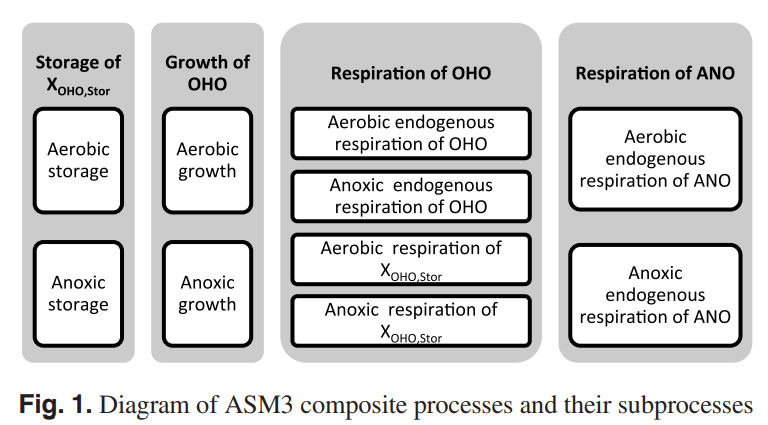
Mathematical modeling of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket reactor in domestic wastewater treatment
This paper introduces a dynamic model to adequately describe an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor. Some available models of a UASB reactor are discussed in order to modify their drawbacks and propose a new improved model with less complexity and more reliability. The developed model is a combination of two recent models introduced in Sweden. According to this model, a UASB rector is divided hydraulically into three compartments with integration of a kinetic model. Simulations are performed to investigate the validity of the developed model which indicates a good agreement with
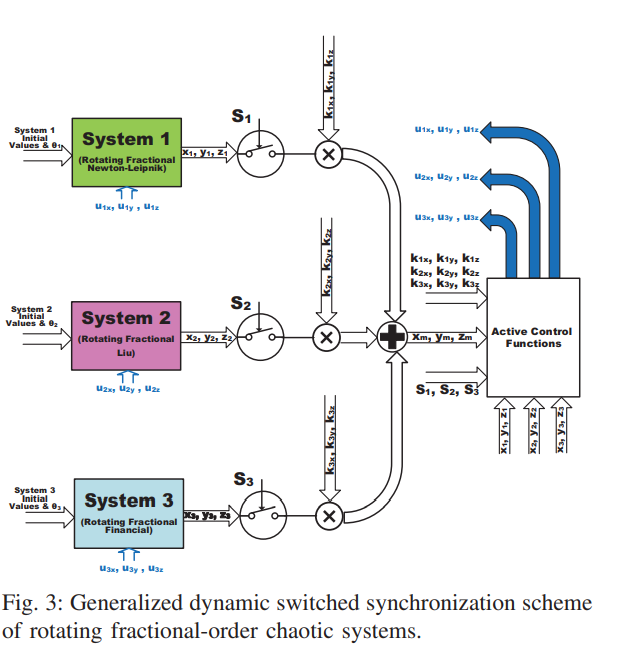
All-Dynamic Synchronization of Rotating Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems
This paper proposes generalized controllable strange attractors through dynamic rotation of fractional-order chaotic systems. Dynamic rotation angle enables the generation of multi-scroll and multi-wing attractors from single and double-scroll ones. The rotating systems are integrated with a generalized dynamic switched synchronization scheme. Dynamic control switches determine whether each system plays the role of master or slave. Based on dynamic scaling factors, the master can be one system or a combination of several ones with new strange attractors. The rotating fractional-order systems
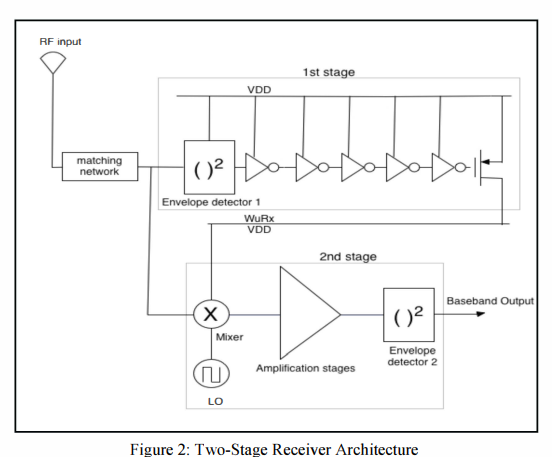
A 2.5 μwatts two stage wake-up receiver for Wireless Sensor Networks
An ultra low power wake-up receiver for Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) applications is presented. The proposed wake-up receiver is composed of two stages. The first stage is a low-power low-sensitivity stage that acts as a 'sentinel' and continuously monitors the channel, while the second stage is a conventional low-power wake-up receiver. The 2.44GHz two-stage receiver has a sensitivity of -72dBm when the transmitted signal power is 0dBm. The power consumed during sleep mode is 2.5μWatts and 41μWatts in the wake-up receiver active mode with a 0.5V supply voltage. The power consumption is
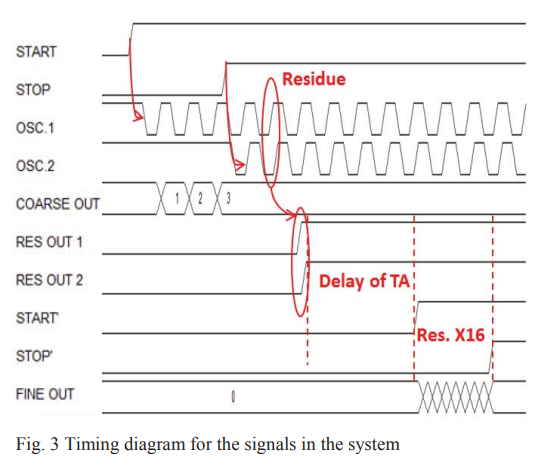
A novel high throughput high resolution two-stage oscillator-based TDC
This paper presents a new technique to reduce the conversion time, hence improve the throughput, of the two-stage Time to Digital Converter (TDC) architecture. An oscillator based TDC is used in the first and second stages. The time residue from the first stage is generated directly after the stop signal is asserted and saved in the form of phase-shift between two oscillating signals. A throughput of 400 MS/s, a DNL of 0.38, and an INL of 0.36 are achieved. © 2013 IEEE.
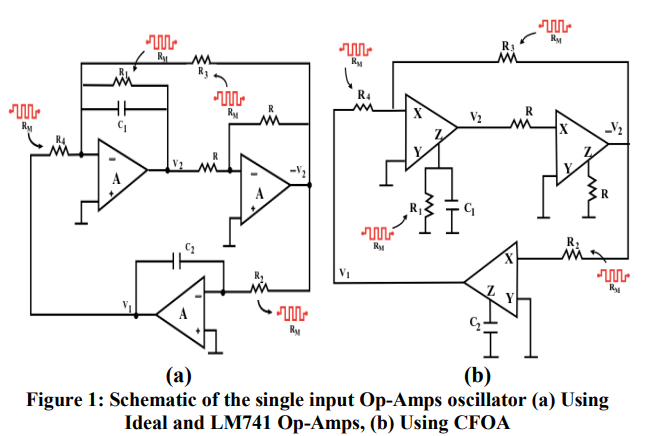
The modified single input Op-Amps memristor based oscillator
This paper introduces the modified single input Op-Amps memristor based oscillator. The oscillator is realized with ideal, LM741 and current feedback (AD844) Op-Amps where memristors replace resistors. The effect of memristor on the oscillation frequency and the oscillation condition that are totally independent is studied. This helped in studying the whole operation regime of the memristor. The effect of initial conditions on the circuit behavior is discussed. The dynamic poles of the oscillator after resistors replacement are illustrated. Sustained oscillation is obtained and simulated
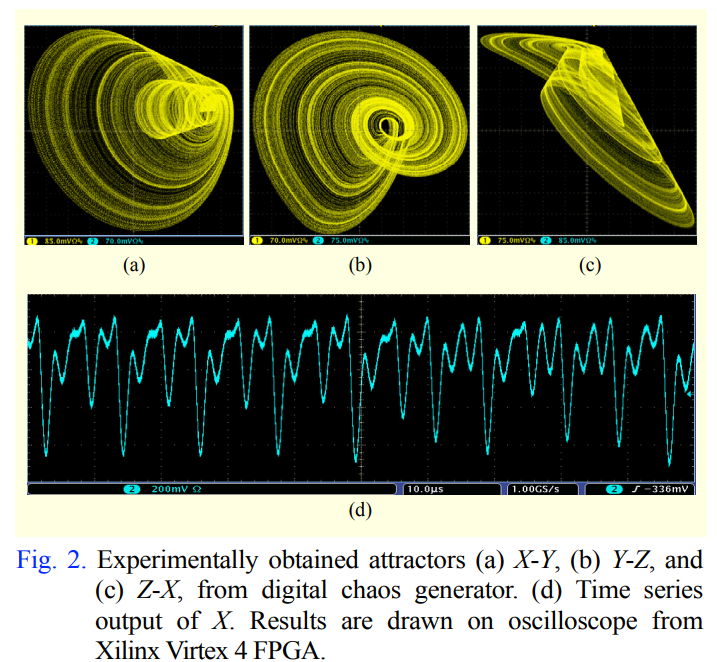
Generalized hardware post-processing technique for chaos-based pseudorandom number generators
This paper presents a generalized post-processing technique for enhancing the pseudorandomness of digital chaotic oscillators through a nonlinear XOR-based operation with rotation and feedback. The technique allows full utilization of the chaotic output as pseudorandom number generators and improves throughput without a significant area penalty. Digital design of a third-order chaotic system with maximum function nonlinearity is presented with verified chaotic dynamics. The proposed post-processing technique eliminates statistical degradation in all output bits, thus maximizing throughput
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››

