Breadcrumb
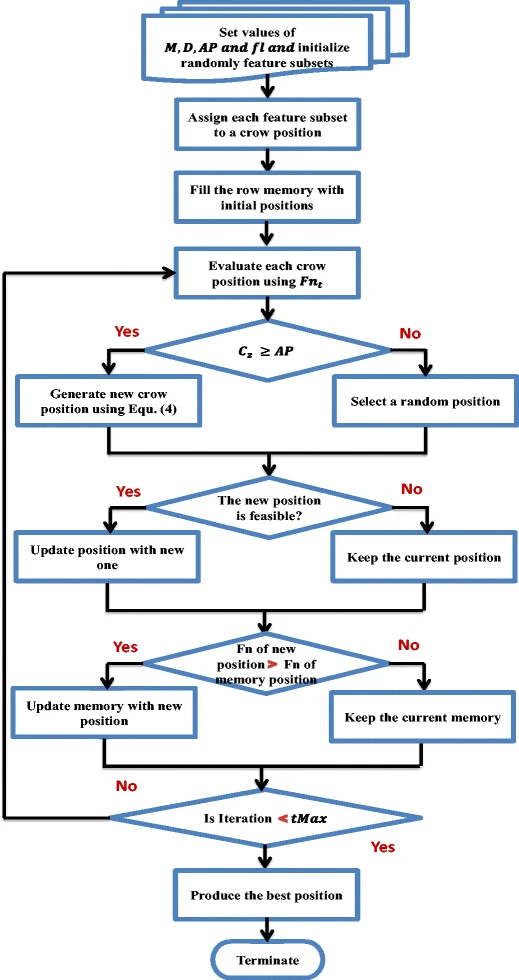
Feature selection via a novel chaotic crow search algorithm
Crow search algorithm (CSA) is a new natural inspired algorithm proposed by Askarzadeh in 2016. The main inspiration of CSA came from crow search mechanism for hiding their food. Like most of the optimization algorithms, CSA suffers from low convergence rate and entrapment in local optima. In this paper, a novel meta-heuristic optimizer, namely chaotic crow search algorithm (CCSA), is proposed to overcome these problems. The proposed CCSA is applied to optimize feature selection problem for 20 benchmark datasets. Ten chaotic maps are employed during the optimization process of CSA. The
Controlled Picard Method for Solving Nonlinear Fractional Reaction–Diffusion Models in Porous Catalysts
This paper discusses the diffusion and reaction behaviors of catalyst pellets in the fractional-order domain as well as the case of nth-order reactions. Two generic models are studied to calculate the concentration of reactant in a porous catalyst in the case of a spherical geometric pellet and a flat-plate particle with different examples. A controlled Picard analytical method is introduced to obtain an approximated solution for these systems in both linear and nonlinear cases. This method can cover a wider range of problems due to the extra auxiliary parameter, which enhances the convergence
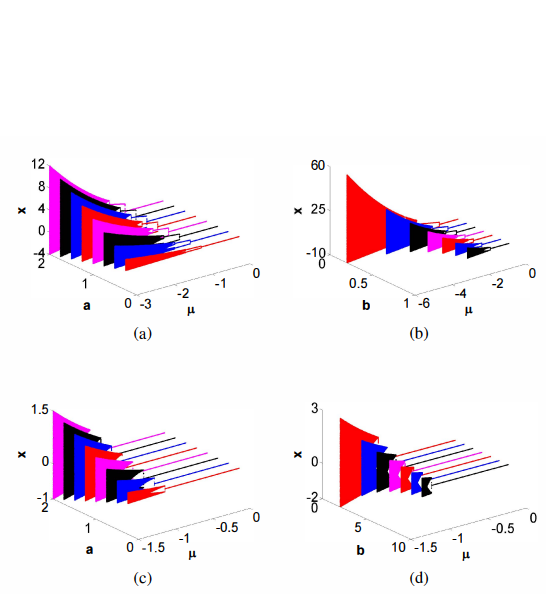
Design of a generalized bidirectional tent map suitable for encryption applications
The discrete tent map is one of the most famous discrete chaotic maps that has widely-spread applications. This paper investigates a set of four generalized tent maps where the conventional map is a special case. The proposed maps have extra degrees of freedom which provide different chaotic characteristics and increase the design flexibility required for many applications. Mathematical analyses for generalized positive and mostly positive tent maps include: bifurcation diagrams relative to all parameters, effective range of parameters, bifurcation points. The maximum Lyapunov exponent (MLE)
Fractional derivative modeling of double-diffusive free convection with von Neumann stability analysis
This paper focuses on the problem of fractional time derivative of fluid flow and convective heat and mass transfer from a heated semi-infinite wall immersed. We provided two cases of study, one is free convective heat transfer and the other is a free double-convective heat and mass transfer. The time-derivative terms in the equations of momentum, energy and concentration are assumed to be fractional using the Grunwald-Letnikov (GL) model. A finite difference scheme has been developed for each case of study and followed by a von Neumann stability analysis. Therefore, a stability condition has
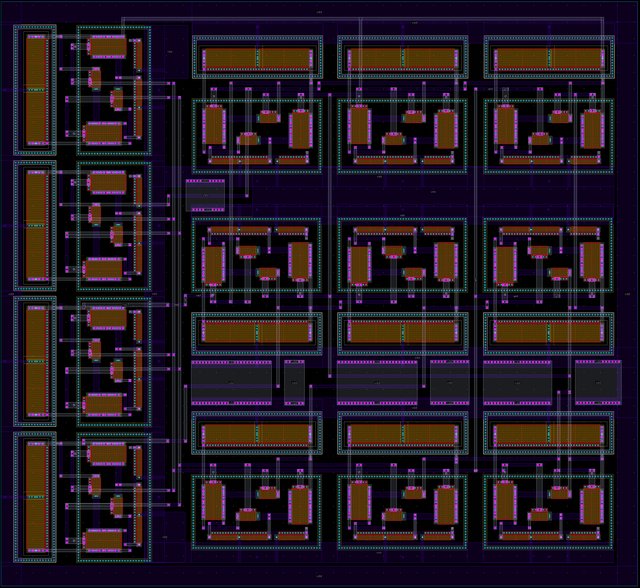
Design of low-voltage FO-[PD] controller for motion systems
Fractional-order controllers have gained significant research interest in various practical applications due to the additional degrees of freedom offered in their tuning process. The main contribution of this work is the analog implementation, for the first time in the literature, of a fractional-order controller with a transfer function that is not directly constructed from terms of the fractional-order Laplacian operator. This is achieved using Padé approximation, and the resulting integer-order transfer function is implemented using operational transconductance amplifiers as active elements
Atmospheric pressure air microplasma current time series for true random bit generation
Generating true random bits of high quality at high data rates is usually viewed as a challenging task. To do so, physical sources of entropy with wide bandwidth are required which are able to provide truly random bits and not pseudorandom bits, as it is the case with deterministic algorithms and chaotic systems. In this work we demonstrate a reliable high-speed true random bit generator (TRBG) device based on the unpredictable electrical current time series of atmospheric pressure air microplasma (APAMP). After binarization of the sampled current time series, no further post-processing was
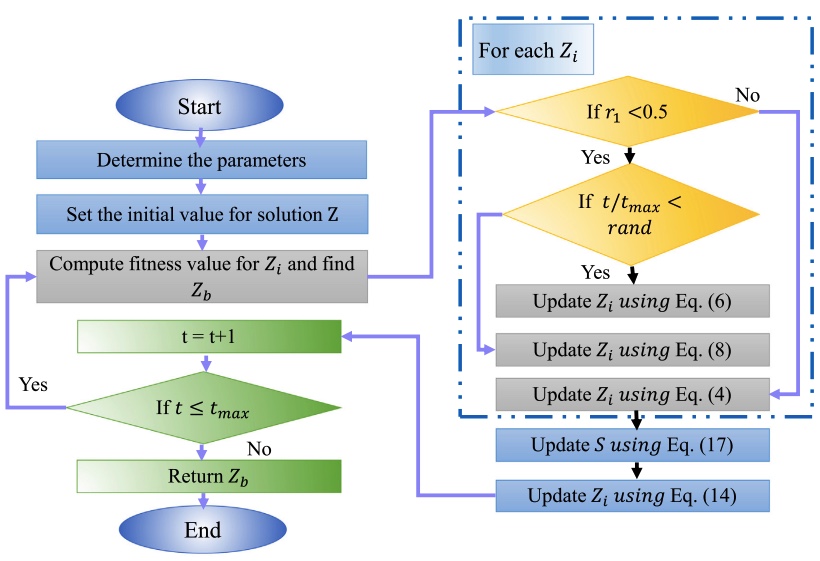
A Grunwald–Letnikov based Manta ray foraging optimizer for global optimization and image segmentation
This paper presents a modified version of Manta ray foraging optimizer (MRFO) algorithm to deal with global optimization and multilevel image segmentation problems. MRFO is a meta-heuristic technique that simulates the behaviors of manta rays to find the food. MRFO established its ability to find a suitable solution for a variant of optimization problems. However, by analyzing its behaviors during the optimization process, it is observed that its exploitation ability is less than exploration ability, which makes MRFO more sensitive to attractive to a local point. Therefore, we enhanced MRFO by
Control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators: A review
In this article, different control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators are presented with two distinguished classes of control strategies in the literature. These are the model-free control and the dynamic control strategy, which is mainly a model-based scheme, and is mostly the alternative when the control requirements are more stringent. The authors strongly believe that this paper will be helpful for researchers and engineers in the field of robotic systems. Copyright 2017 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
Further experimental evidence of the fractional-order energy equation in supercapacitors
Due to the dispersive porous nature of its material, carbon–carbon supercapacitors have a current–voltage relationship which is modeled by a fractional-order differential equation of the form i(t)=Cα[Formula presented] where α≤1 is a dispersion coefficient and Cα is a pseudo-capacitance not measurable in Farads. Hence, the energy stored in a capacitor, known to equal CV2/2 where C is the capacitance in Farad and V is the voltage applied, does not apply to a supercapacitor. In a recent work (Allagui et al., 2016), a fractional-order energy equation that enables the quantification of the energy
Fuzzy firefly clustering for tumour and cancer analysis
Swarm intelligence represents a meta-heuristic approach to solve a wide variety of problems. Searching for similar patterns of genes is becoming very essential to predict the expression of genes under various conditions. Firefly clustering inspired by the behaviour of fireflies helps in grouping genes that behave alike. Contrasting hard clustering methodology, fuzzy clustering assigns membership values for every gene and predicts the possibility of belonging to every cluster. To distinguish highly expressed and suppressed genes, the research in this paper proposes an efficient fuzzy-firefly
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››

