Atmospheric pressure air microplasma current time series for true random bit generation
Generating true random bits of high quality at high data rates is usually viewed as a challenging task. To do so, physical sources of entropy with wide bandwidth are required which are able to provide truly random bits and not pseudorandom bits, as it is the case with deterministic algorithms and chaotic systems. In this work we demonstrate a reliable high-speed true random bit generator (TRBG) device based on the unpredictable electrical current time series of atmospheric pressure air microplasma (APAMP). After binarization of the sampled current time series, no further post-processing was
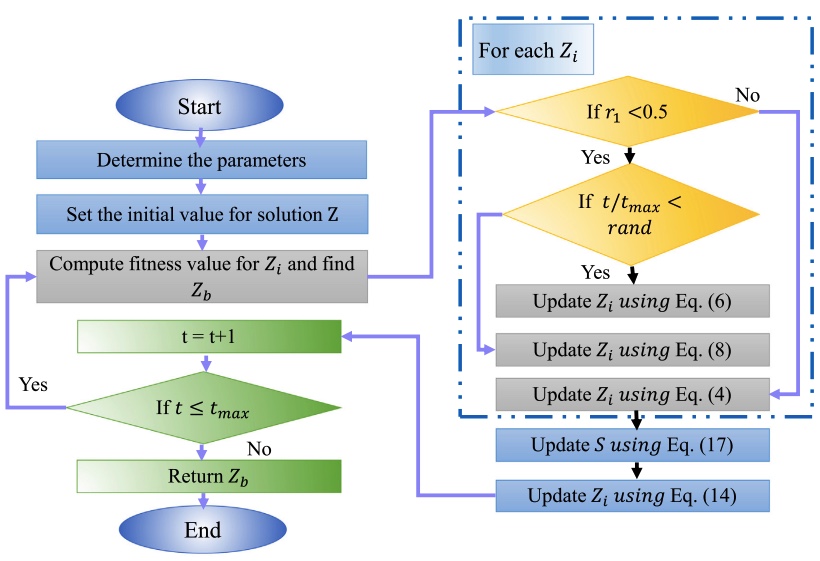
A Grunwald–Letnikov based Manta ray foraging optimizer for global optimization and image segmentation
This paper presents a modified version of Manta ray foraging optimizer (MRFO) algorithm to deal with global optimization and multilevel image segmentation problems. MRFO is a meta-heuristic technique that simulates the behaviors of manta rays to find the food. MRFO established its ability to find a suitable solution for a variant of optimization problems. However, by analyzing its behaviors during the optimization process, it is observed that its exploitation ability is less than exploration ability, which makes MRFO more sensitive to attractive to a local point. Therefore, we enhanced MRFO by
Control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators: A review
In this article, different control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators are presented with two distinguished classes of control strategies in the literature. These are the model-free control and the dynamic control strategy, which is mainly a model-based scheme, and is mostly the alternative when the control requirements are more stringent. The authors strongly believe that this paper will be helpful for researchers and engineers in the field of robotic systems. Copyright 2017 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
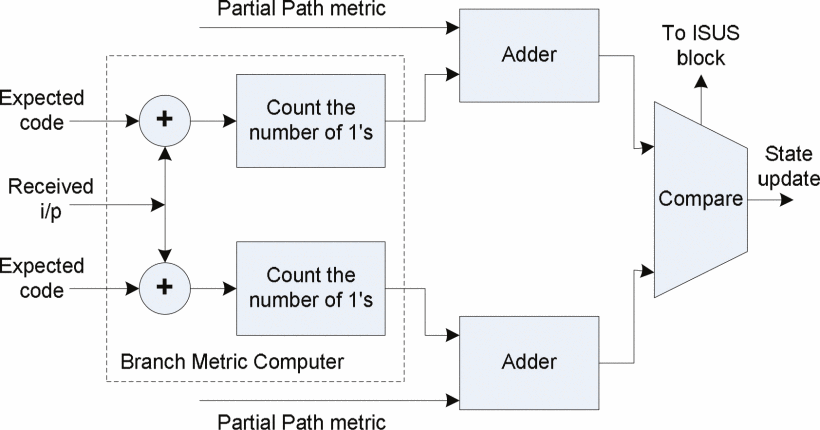
FPGA implementation of a reconfigurable Viterbi decoder for WiMAX receiver
Field Programmable Gate Array technology (FPGA) is a highly configurable option for implementing many sophisticated signal processing tasks in Software Defined Radios (SDRs). Those types of radios are realized using highly configurable hardware platforms. Convolutional codes are used in every robust digital communication system and Viterbi algorithm is employed in wireless communications to decode the convolutional codes. Such decoders are complex and dissipate large amount of power. In this paper, a low power-reconfigurable Viterbi decoder for WiMAX receiver is described using a VHDL code for
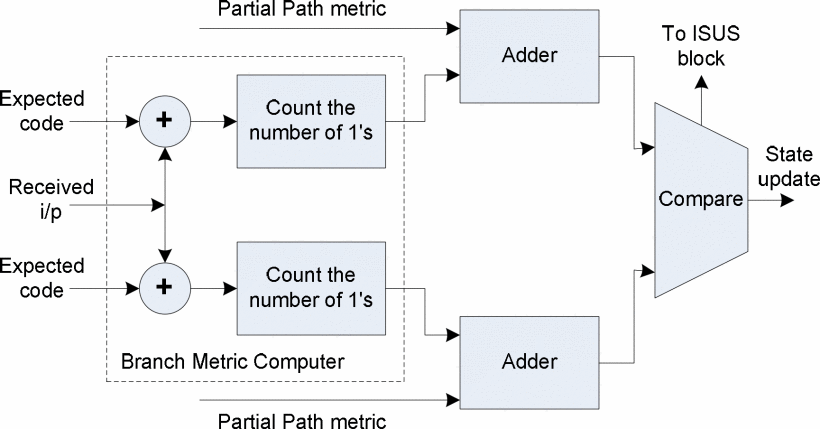
FPGA implementation of a configurable viterbi decoder for software radio receiver
Convolutional codes are one of the Forward Error Correction (FEC) codes that are used in every robust digital communication system. Viterbi algorithm is employed in wireless communications to decode the convolutional codes. Such decoders are complex and dissipate large amount of power. Software Defined Radio (SDR) is realized using highly configurable hardware platforms. Field Programmable Gate Array technology (FPGA) is a highly configurable option for implementing many sophisticated signal processing tasks in SDR. In this paper, a generic, configurable and low power Viterbi decoder for
Fibonacci-based hardware post-processing for non-autonomous signum hyperchaotic system
This paper presents a hardware implementation of a robust non-autonomous hyperchaotic-based PRNG driven by a 256-bit LFSR. The original chaotic output is post-processed using a novel technique based on the Fibonacci series, bitwise XOR, rotation, and feedback. The proposed post-processing technique preserves the throughput of the system and enhances the randomness in the output which is verified by successfully passing all NIST SP. 800-22 tests. The system is realized on a Xilinx Virtex 4 FPGA achieving throughput up to 13.165 Gbits/s for 16-bit bus-width surpassing previously reported CB
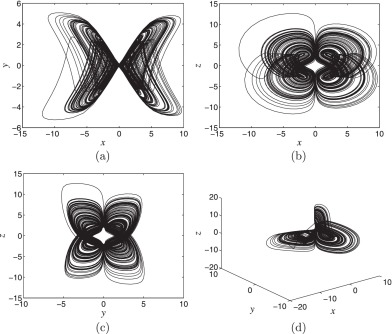
Four-wing attractors in a novel chaotic system with hyperbolic sine nonlinearity
Chaotic systems generating multi-wing attractors have received considerable attention in the literature. In this work, we propose a novel three-dimensional chaotic system with hyperbolic sine nonlinearity. It is worth noting that the system is elegant and includes only one parameter. Despite its simple structure, the new system displays double-wing and four-wing chaotic attractors. By studying dynamics of the system, coexistence of limit cycles or chaotic attractors is discovered. The capable of the synchronization of new chaotic system is verified by using an adaptive control. Furthermore, an
Chaos-based hardware speech encryption scheme using modified tent map and bit permutation
This paper proposes a speech encryption scheme based on a generalized modified chaotic tent map and bit permutation and presents its hardware realization. The generalization scales the output range and increases the key space. The modification controls the bounds on the output range through a parameter such that chaotic output exists for almost all values of the parameter. The security and efficiency of the speech encryption scheme are validated through the randomness of the encrypted signal, the key sensitivity and the hardware resources utilization. The proposed scheme utilizes less FPGA
FPGA realization of speech encryption based on modified chaotic logistic map
This paper presents an FPGA design and implementation of a chaotic speech encryption and decryption system based on bit permutations. Different encryption schemes are realized and compared. In addition, various testing methods including entropy, mean squared error, and correlation coefficients are used to analyze the efficiency of the system. The techniques for area and delay minimization are used. Carry look-ahead adder, multi-operand adder and booth multiplier are used to improve the performance of the encryption schemes design. A comparison between the different encryption architectures and
FPGA realization of a speech encryption system based on a generalized modified chaotic transition map and bit permutation
This paper proposes a generalized modified chaotic transition map with three independent parameters. A hardware speech encryption scheme utilizing this map along with a bit permutation network is presented. While the transition map’s generalization introduces additional parameters, the modification enhances its chaotic properties and overcomes the finite range of the control parameter and dynamical degradation problems. The modification also presents a simplification for the hardware realization of the exponentiation operation in the map’s equation because the modified output range allows
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 54
- Next page ››
