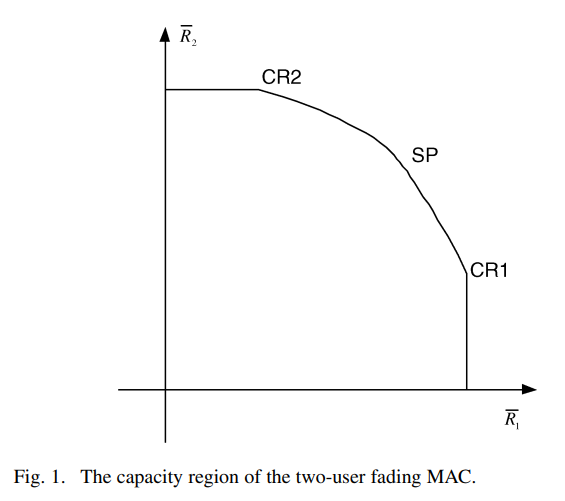
The water-filling game in fading multiple-access channels
A game-theoretic framework is developed to design and analyze the resource allocation algorithms in fading multiple-access channels (MACs), where the users are assumed to be selfish, rational, and limited by average power constraints. The maximum sum-rate point on the boundary of the MAC capacity region is shown to be the unique Nash equilibrium of the corresponding water-filling game. This result sheds a new light on the opportunistic communication principle. The base station is then introduced as a player interested in maximizing a weighted sum of the individual rates. A Stackelberg
Coagulation/flocculation process for textile mill effluent treatment: experimental and numerical perspectives
This study investigates the feasibility of applying coagulation/flocculation process for real textile wastewater treatment. Batch experiments were performed to detect the optimum performance of four different coagulants; Ferric Sulphate (Fe2(SO4)3), Aluminium Chloride (AlCl3), Aluminium Sulphate (Al2(SO4)3) and Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) at diverse ranges of pH (1–11) on the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), colour, total nitrogen (TN) and turbidity from real textile wastewater. At pH 9, FeCl3 demonstrated the most effective removal for all studied
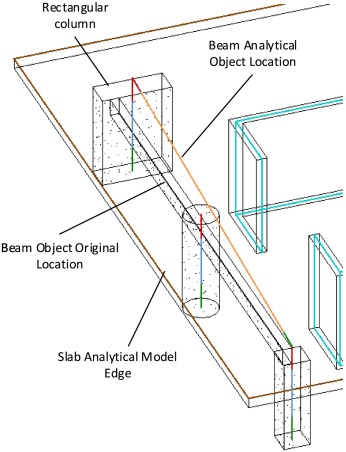
Geometrically accurate structural analysis models in BIM-centered software
Current BIM models impose restrictions on the geometry of building members in their analytical models, where components are fitted to wireframe representations. This unnecessary reduction in geometrical representation drives the loss of structural details and may lead to defective structural analysis. The present paper addresses the current shortcomings in the semantics of analytical models within BIM environments and recommends enhancements. An explanation is given of a BIM-centered structural analysis system based on coupling finite elements for vertical and horizontal elements, and boundary
Cole bio-impedance model variations in daucus carota sativus under heating and freezing conditions
This paper reports on the variations in the parameters of the single dispersion Cole bio-impedance model of Daucus Carota Sativus (carrots) under heating and freezing conditions. Experiments are conducted on six samples with recorded live bio-impedance spectra versus temperature. The Cole model parameters are extracted from the measured data using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA) optimization technique and their variations are correlated with well-known bio-chemical and bio-mechanical variations. This represents a non-invasive method for characterizing and measuring the degree of change
Two implementations of fractional-order relaxation oscillators
This work proposes general formulas for designing two different topologies of fractional-order relaxation oscillators. One topology contains an Operational Amplifier and the other one relies on an Operational Trans-Resistance Amplifier. The design procedure hinges on the general fractional-order natural and step responses of RC, which is proved in this work depending on Mittag Leffler function. The proposed topologies can be controlled to generate symmetrical and non-symmetrical square wave signals. They also benefit from the employment of fractional-order capacitors (FOCs), which makes it
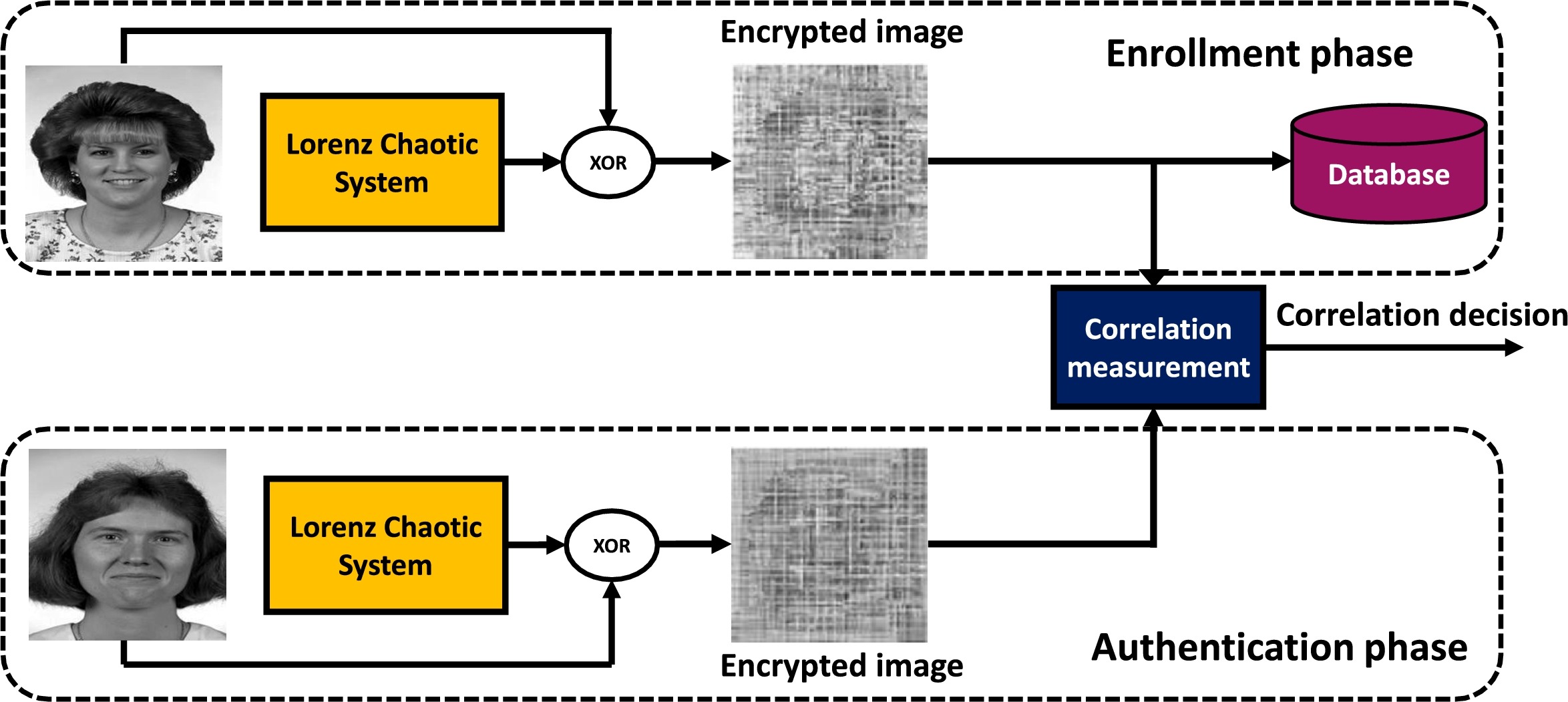
Cancellable face recognition based on fractional-order Lorenz chaotic system and Haar wavelet fusion
Cancellable biometrics is the art of generating distorted or encrypted templates of original biometric templates. The evolution of cancellable biometrics is attributed to the advanced hacking technologies that can capture the original stored biometrics from databases. One of the solutions for this problem is to store cancellable biometric templates in the database rather than the original ones. This paper presents a cancellable face recognition scheme that is based on face image encryption with Fractional-Order (FO) Lorenz chaotic system. The basic idea is to generate user-specific random keys
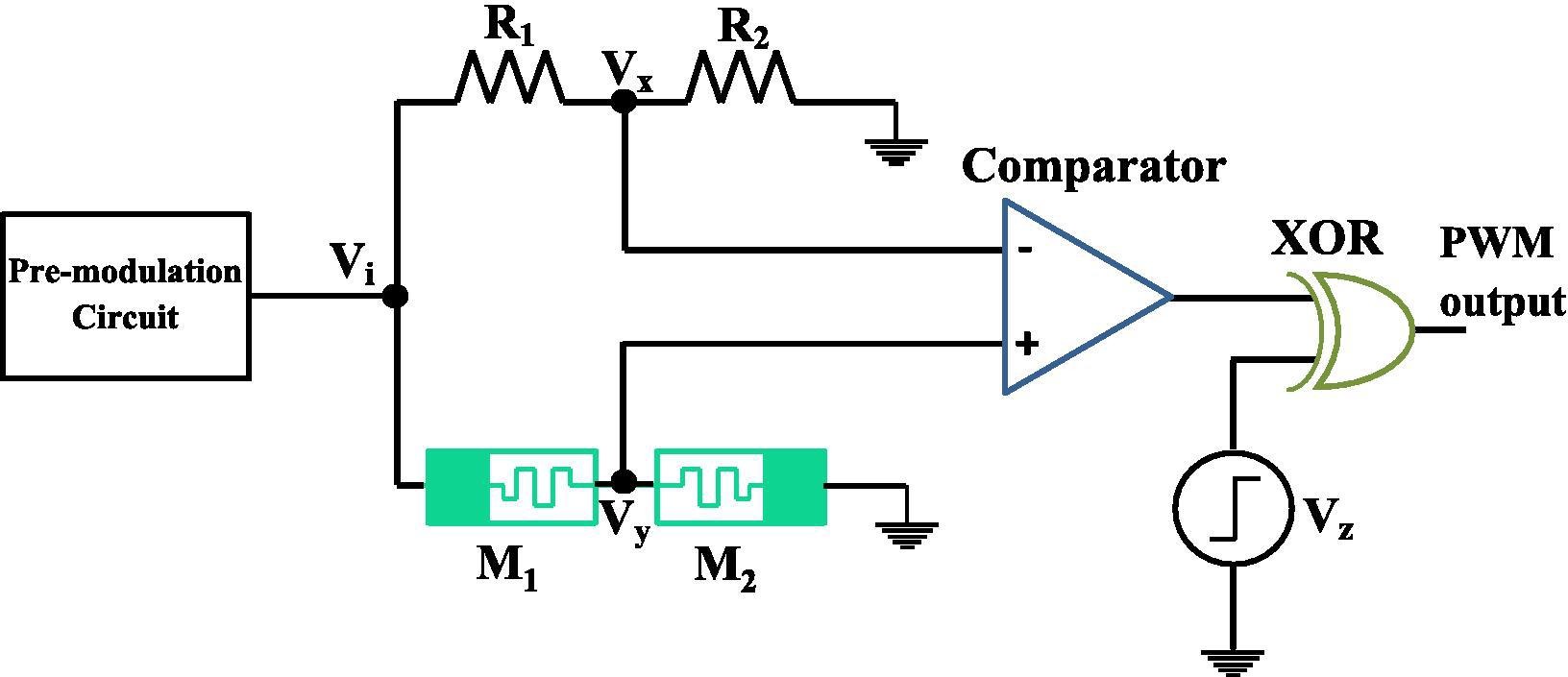
Center pulse width modulation implementation based on memristor
This paper introduces two new versions for memristor-based center pulse-width modulator (PWM) circuits. The proposed circuits use only one comparator which reduces the circuit complexity and power dissipation compared to a former work. The first design is based on two memristors and two resistors while the second design is based on four memristors. Theoretical analysis is provided, and the numerical solution is handled on MATLAB. Simulation is carried out on Cadence software, and the results follow the theoretical analysis. The experiment is implemented using commercial off-the-shelf
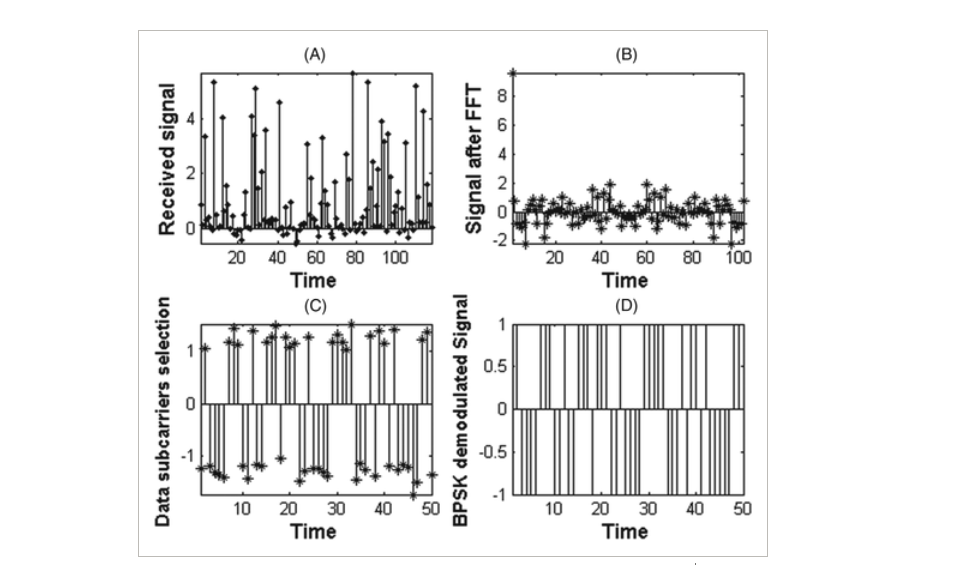
Odd clipping optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing for VLC system
The Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) has emerged as one of the promising techniques because of its robustness to multipath fading with high-speed data transmission. Classical bipolar OFDM cannot be used in intensity modulated with direct detection (IM/DD) optical communication systems, as visible light communication (VLC), so many optical modulation techniques as asymmetrical clipped optical OFDM (ACO-OFDM) and DC-Clipped OFDM (DCO-OFDM) have been investigated. In this paper, we introduce a novel optical modulation scheme that meets the optical communications requirements. The
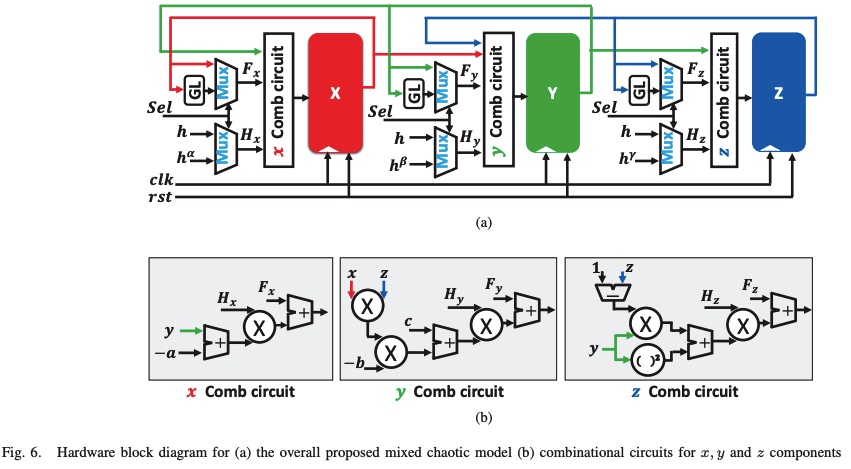
A Digital Hardware Implementation for A new Mixed-Order Nonlinear 3-D Chaotic System
This paper introduces a generic modeling for a 3-D nonlinear chaotic based on fractional-order mathematical rules. Also, a novel modeling for the system using a mixture between integer and fractional-order calculus is proposed. Dynamics of the new realization are illustrated using phase portrait diagrams with complex behavior. Also, a great change in the parameter ranges is investigated using bifurcation diagrams. MATLAB and Xilinx ISE 14.5 are used in system simulations. Furthermore, the digital hardware implementation is done using Xilinx FPGA Virtex-5 kit. The synthesis report shows that
Study of optical power variations in multi-layer human skin model for monitoring the light dose
Monitoring light dose is essential in much clinical procedures like bio-stimulation, neuro-medicine and photodynamic therapy and in many biophotonics applications such as optogenetics and biosensing. However, monitoring the optical power dissipation as light travels in different layers of tissue is essential in determining the required optical dose. Each part in the human body is protected by different thickness of skin layer; therefore, studying the variations of the optical power when light propagates in different thicknesses of the human skin is essential for safe and accurate medical
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 37
- Next page ››
