Graph transformer for communities detection in social networks
Graphs are used in various disciplines such as telecommunication, biological networks, as well as social networks. In large-scale networks, it is challenging to detect the communities by learning the distinct properties of the graph. As deep learning has made contributions in a variety of domains, we try to use deep learning techniques to mine the knowledge from large-scale graph networks. In this paper, we aim to provide a strategy for detecting communities using deep autoencoders and obtain generic neural attention to graphs. The advantages of neural attention are widely seen in the field of
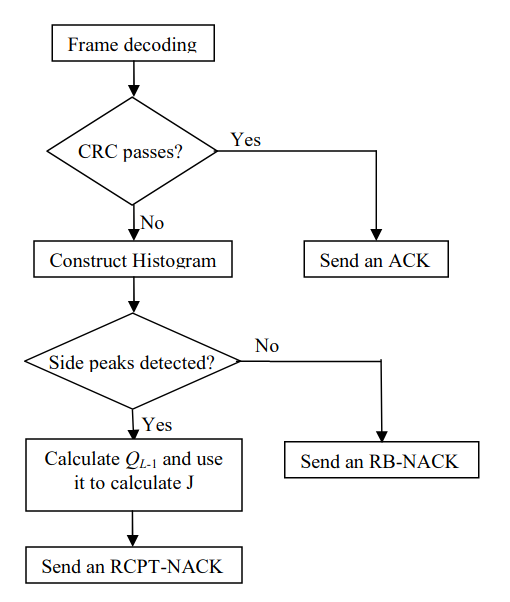
Novel reliability-based hybrid ARQ technique
In this paper we propose a novel technique for hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) systems where turbo codes are used as the forward error correction (FEC) techniques. This technique uses the histogram of the soft values generated by the turbo decoder to control the size and the contents of the retransmissions needed when the packet can not be decoded correctly. These soft values represent the reliabilities of the information bits; hence the proposed technique is a reliability-based (RB) HARQ technique. The proposed technique is compared to the conventional RB-HARQ and the conventional rate
Asymmetric degrees of freedom of the full-duplex MIMO 3-way channel
In this paper, we characterize the asymmetric total degrees of freedom (DoF) of a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) 3-way channel. Each node has a separate-antenna full-duplex MIMO transceiver with a different number of antennas, where each antenna can be configured for either signal transmission or reception. Each node has two unicast messages to be delivered to the two other nodes. We first derive upper bounds on the total DoF of the system. Cut-set bounds in conjunction with genie-aided bounds are derived to characterize the achievable total DoF. Afterwards, we analytically derive the
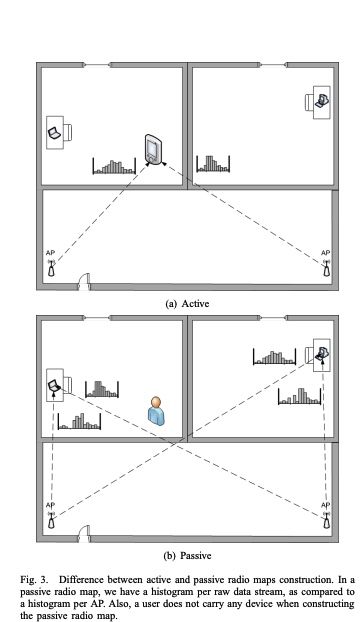
A deterministic large-scale device-free passive localization system for wireless environments
The widespread usage of wireless local area networks and mobile devices has fostered the interest in localization systems for wireless environments. The majority of research in the context of wirelessbased localization systems has focused on device-based active localization, in which a device is attached to tracked entities. Recently, device-free passive localization (DfP) has been proposed where the tracked entity is neither required to carry devices nor participate actively in the localization process. DfP systems are based on the fact that RF signals are affected by the presence of people

Enhanced Success History Adaptive de for Parameter Optimization of Photovoltaic Models
In the past few decades, a lot of optimization methods have been applied in estimating the parameter of photovoltaic (PV) models and obtained better results, but these methods still have some deficiencies, such as higher time complexity and poor stability. To tackle these problems, an enhanced success history adaptive DE with greedy mutation strategy (EBLSHADE) is employed to optimize parameters of PV models to propose a parameter optimization method in this paper. In the EBLSHADE, the linear population size reduction strategy is used to gradually reduce population to improve the search

Single-Objective Real-Parameter Optimization: Enhanced LSHADE-SPACMA Algorithm
Real parameter optimization is one of the active research fields during the last decade. The performance of LSHADE-SPACMA was competitive in IEEE CEC’2017 competition on Single Objective Bound Constrained Real-Parameter Single Objective Optimization. Besides, it was ranked fourth among twelve papers were presented on and compared to this new benchmark problems. In this work, an improved version named ELSHADE-SPACMA is introduced. In LSHADE-SPACMA, p value that controls the greediness of the mutation strategy is constant. While in ELSHADE-SPACMA, p value is dynamic. Larger value of p will
Proactive Caching for Vehicular Ad hoc Networks Using the City Model
Caching at Roadside Units (RSUs) is a promising technique to alleviate the load on network backhaul in Vehicular AdHoc Networks (VANETs). It also allows us to minimize communications latency between RSUs and connected vehicles, which are interested in massive multimedia contents. This work proposes novel proactive caching schemes at RSUs for the city mobility environment. We adopt the Manhattan city model, where streets are arranged in an organized manner and movable nodes are allowed to traverse along the grid of horizontal and vertical streets. Exploiting the information about vehicles
Decentralized coded caching in wireless networks: Trade-off between storage and latency
This paper studies the decentralized coded caching for a Fog Radio Access Network (F-RAN), whereby two edge-nodes (ENs) connected to a cloud server via fronthaul links with limited capacity are serving the requests of K r users. We consider all ENs and users are equipped with caches. A decentralized content placement is proposed to independently store contents at each network node during the off-peak hours. After that, we design a coded delivery scheme in order to deliver the user demands during the peak-hours under the objective of minimizing the normalized delivery time (NDT), which refers
Proactive cognitive networks with predictable demand
In this paper we characterize the proactive diversity gain of a cognitive network with predictable primary and secondary requests. Network performance is analyzed under two proposed proactive service policies that preserve higher priority for the primary user. The first policy preserves the primary diversity bound as if there is no secondary user in the network, whereas the second policy boosts the secondary diversity with guaranteed higher primary diversity. For each policy, we derive diversity gain bounds for primary and secondary users. We show that the predictability of secondary requests
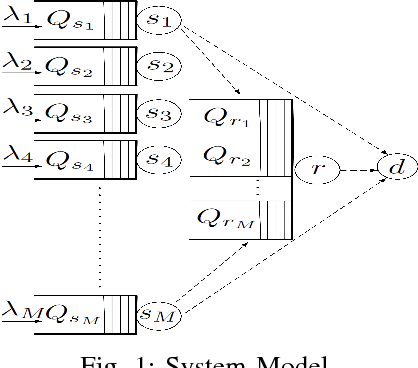
A hybrid TDMA-MAC cooperative relaying scheme: Stability and delay analysis
We consider a cooperative relaying system with any number of source terminals, one shared relay, and a common destination. We assume a slotted time division multiple access (TDMA) framework in which each source terminal is allocated a fraction of the time. We propose a novel hybrid cooperative scheme for the described network. In contrast to former works which assume that the relay only transmits in the idle time slots, we assume that the relay can, simultaneously, transmit with the source terminals via multi-access channel (MAC). In the hybrid cooperative scheme, the relay operates in two
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 16
- Next page ››
