Natcracker: Nat combinations matter
In this paper, we report our experience in working with Network Address Translators (NATs). Traditionally, there were only 4 types of NATs. For each type, the (im)possibility of traversal is well-known. Recently, the NAT community has provided a deeper dissection of NAT behaviors resulting into at least 27 types and documented the (im)possibility of traversal for some types. There are, however, two fundamental issues that were not previously tackled by the community. First, given the more elaborate set of behaviors, it is incorrect to reason about traversing a single NAT, instead combinations
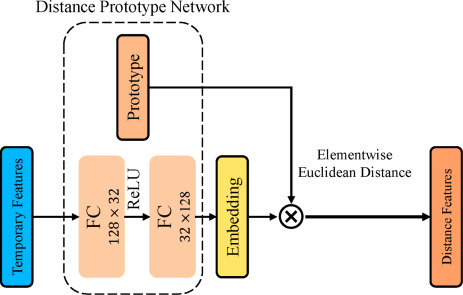
Multiple classifiers for time series classification using adaptive fusion of feature and distance based methods
Time series classification is a supervised learning problem used in many vital applications. Classification of data varying with time is considered an important and challenging pattern recognition task. The temporal aspect and lack of features in time series data makes the learning process different from traditional classification problems. In this paper we propose a multiple classifier system approach for time series classification. The proposed approach adaptively integrates extracted local and global features together with distance similarity based methods. A feature extraction process is
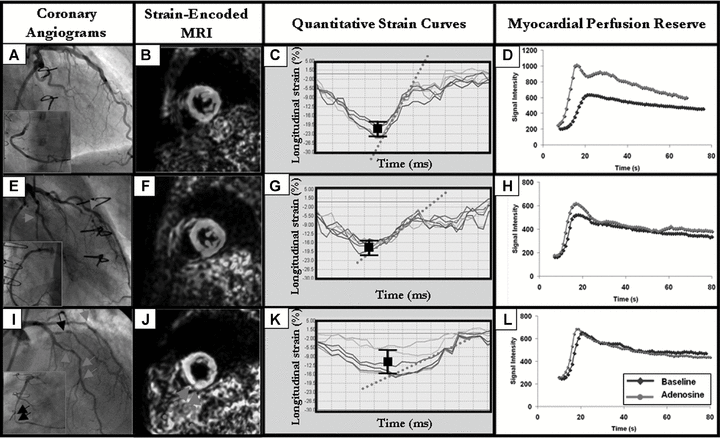
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance for the evaluation of chronic allograft vasculopathy in transplant recipients
The aim of our study was to investigate the ability of Strain-Encoded magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) in heart transplantation (HTx)-recipients. In consecutive subjects (n = 69), who underwent cardiac catheterization, MRI was performed for quantification of myocardial strain and perfusion reserve. Based on angiographic findings subjects were classified: group A including patients with normal vessels; group B, patients with stenosis
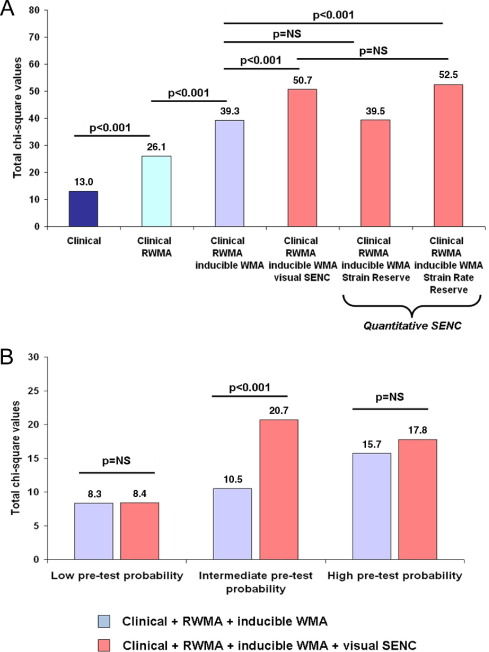
Strain-encoded cardiac magnetic resonance during high-dose dobutamine stress testing for the estimation of cardiac outcomes: Comparison to Clinical Parameters and Conventional Wall Motion Readings
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the prognostic value of strain-encoded magnetic resonance imaging (SENC) during high-dose dobutamine stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (DS-MRI) compared with conventional wall motion readings. Background: Detection of inducible ischemia by DS-MRI on the basis of assessing cine images is subjective and depends on the experience of the readers, which may influence not only the diagnostic classification but also the risk stratification of patients with ischemic heart disease. Methods: In all, 320 consecutive patients with suspected or

Multi-view human action recognition system employing 2DPCA
A novel algorithm for view-invariant human action recognition is presented. This approach is based on Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) applied directly on the Motion Energy Image (MEI) or the Motion History Image (MHI) in both the spatial domain and the transform domain. This method reduces the computational complexity by a factor of at least 66, achieving the highest recognition accuracy per camera, while maintaining minimum storage requirements, compared with the most recent reports in the field. Experimental results performed on the Weizmann action and the INIRIA IXMAS
Multiplicity per rapidity in Carruthers and hadron resonance gas approaches
The multiplicity per rapidity of the well-identified particles π-, π+, k-, k+, p¯ , p, and p- p¯ measured in different high-energy experiments, at energies ranging from 6.3 to 5500 GeV, is successfully compared with the Cosmic Ray Monte Carlo event generator. For these rapidity distributions, we introduce a theoretical approach based on fluctuations and correlations (Carruthers approach) and another one based on statistical thermal assumptions (hadron resonance gas approach). Both approaches are fitted to both sets of results deduced from experiments and simulations. We found that the
In silico identification of potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer
Background: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide and is the most commonly diagnosed cancer. Like other cancers, it is a complex and highly heterogeneous disease involving multiple signaling pathways. Identifying potential therapeutic targets is critical for the development of effective treatment strategies. Methods: We used a systems biology approach to identify potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer. We first identified genes that were differentially expressed between smokers with normal lungs and those with cancerous lungs, then integrated

Labour productivity in building construction: A field study
This paper describes a field study conducted over a period of 11-months on labour productivity observed during the construction of a new university campus in Cairo, Egypt. The campus is being built on 127 acres and the field study was conducted during the construction of two main buildings; each of 20,000 m 2 built up area. The study utilized work sampling (WS), craftsman questionnaire (CQ), and foreman delay survey (FDS) methods to analyze labour productivity of three indicative and labour-intensive trades, namely formwork, masonry work, and HVAC duct installation. The results were also
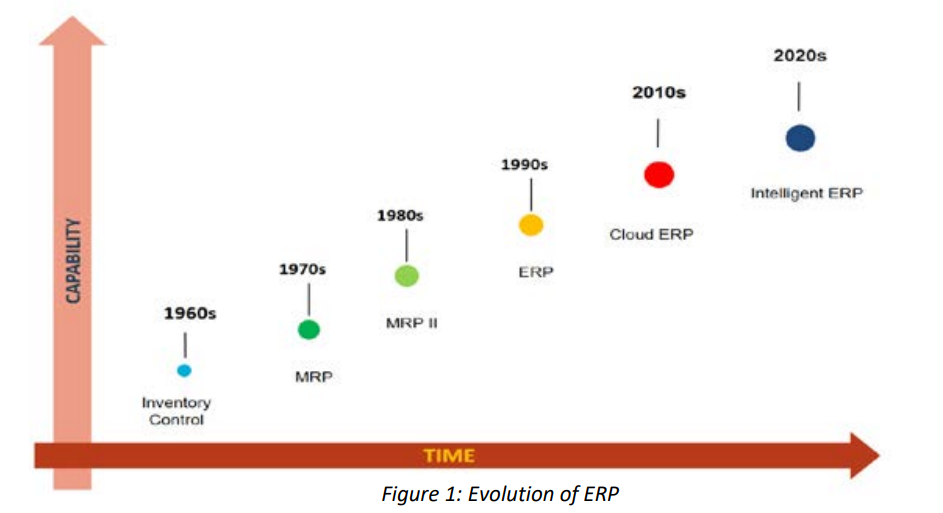
Guidelines for selecting emerging technology features for cloud erp
Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT) permeate every aspect of work and life. For example, in the supply chain management: IoT-networked sensors can provide real-time insight into the provenance of goods and materials, supplier performance, available capacity, predictive demand and other key data. In turn, this data can feed autonomous and intelligent processes that “learn” how to respond to changing circumstances. Classical ERP systems do not support this distributed innovation. Emerging Technologies in Cloud ERP are what brings
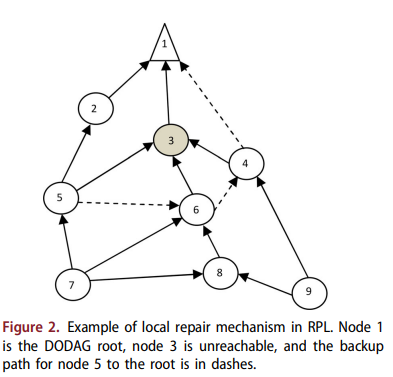
Optimal proactive monitor placement & scheduling for IoT networks
This work is fulfilled in the context of the optimized monitoring of Internet of Things (IoT) networks. IoT networks are faulty; Things are resource-constrained in terms of energy and computational capabilities; they are also connected via lossy links. For IoT systems performing a critical mission, it is crucial to ensure connectivity, availability, and network reliability, which requires proactive network monitoring. The idea is to oversee the network state and functioning of the nodes and links; to ensure the early detection of faults and decrease node-unreachability times. It is imperative
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
