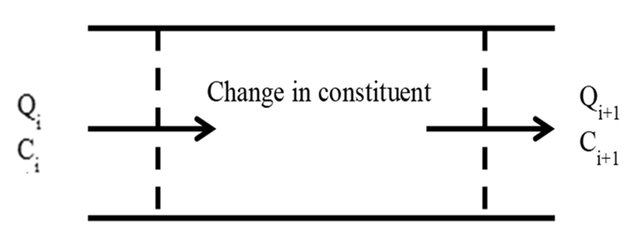
Determining the effect of changing channel geometry of irrigation canals on dissolved oxygen concentration
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is an important water quality parameter. It is considered the most important parameter. DO concentration in water is affected by different parameters such as volume flow rate, water velocity, and re-aeration rate. Those parameters are directly affected by the geometry of the waterway. Thus, studying the impact of changing channel geometry on DO is very important. Many researchers studied the effect of influential parameters on water quality variables but the influence of channel geometric parameters on DO was not studied thoroughly before. This research aims to study the
Multiplicity per rapidity in Carruthers and hadron resonance gas approaches
The multiplicity per rapidity of the well-identified particles π-, π+, k-, k+, p¯ , p, and p- p¯ measured in different high-energy experiments, at energies ranging from 6.3 to 5500 GeV, is successfully compared with the Cosmic Ray Monte Carlo event generator. For these rapidity distributions, we introduce a theoretical approach based on fluctuations and correlations (Carruthers approach) and another one based on statistical thermal assumptions (hadron resonance gas approach). Both approaches are fitted to both sets of results deduced from experiments and simulations. We found that the

Labour productivity in building construction: A field study
This paper describes a field study conducted over a period of 11-months on labour productivity observed during the construction of a new university campus in Cairo, Egypt. The campus is being built on 127 acres and the field study was conducted during the construction of two main buildings; each of 20,000 m 2 built up area. The study utilized work sampling (WS), craftsman questionnaire (CQ), and foreman delay survey (FDS) methods to analyze labour productivity of three indicative and labour-intensive trades, namely formwork, masonry work, and HVAC duct installation. The results were also
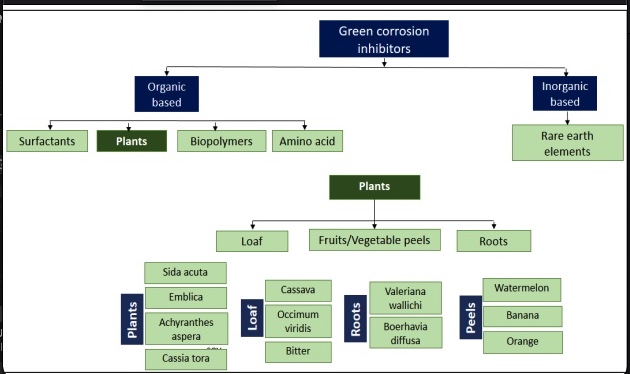
A critical review on green corrosion inhibitors based on plant extracts: Advances and potential presence in the market
Corrosion occurs in all sectors including oil pipelines, drinking water and sewerage in the majority of cases linked to corrosion of steel. Good corrosion management includes optimising corrosion control actions and minimising lifecycle corrosion costs whilst meeting environmental goals. The toxicity of commonly used synthetic inhibitors are the subject of recent legislations (REACH and PARCOM) have led to search on more eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors. Extensive research is conducted to assess the corrosion inhibition rate of diverse green inhibitors. However, it was not adequately
A step forward enhancing green buildings in developing countries
Sustainability is essential for maintaining certain levels of life quality for next generations. Accordingly, Egypt started to establish its own rating system to achieve sustainable development. There are several green building rating systems that are recently used such as: The LEED (Leadership in energy and environmental Design) rating system, Green Pyramid Rating System “GPRS”, and TARSHEED rating system. GPRS and LEED are almost the same since GPRS is based on LEED. Due to the significant cultural and environmental changes between Egypt and the United States, LEED rating system cannot be
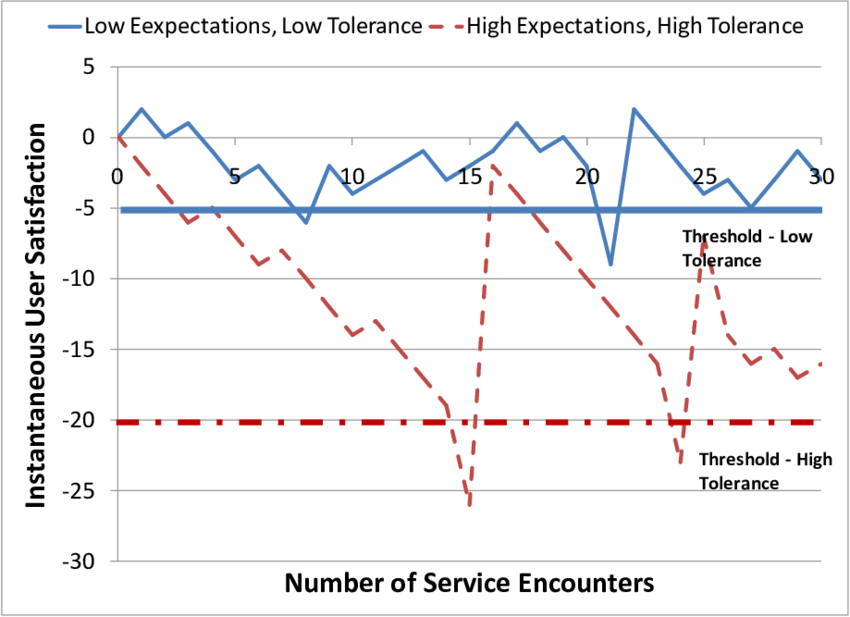
Modeling user behavior and infrastructure level of service: An agent-based simulation approach
Traditional modeling frameworks used for infrastructure asset management have suffered from two main shortcomings. Most approaches have focused their modeling efforts on the infrastructure asset itself, thereby ignoring the multitude of interactions that occur between other entities. In addition, an a-priori behavior of all elements in the modeling environment has always been assumed. This paper argues that these shortcomings have significantly limited the decision-making capabilities of infrastructure asset management systems by limiting their ability to simulate emergent behavior that is
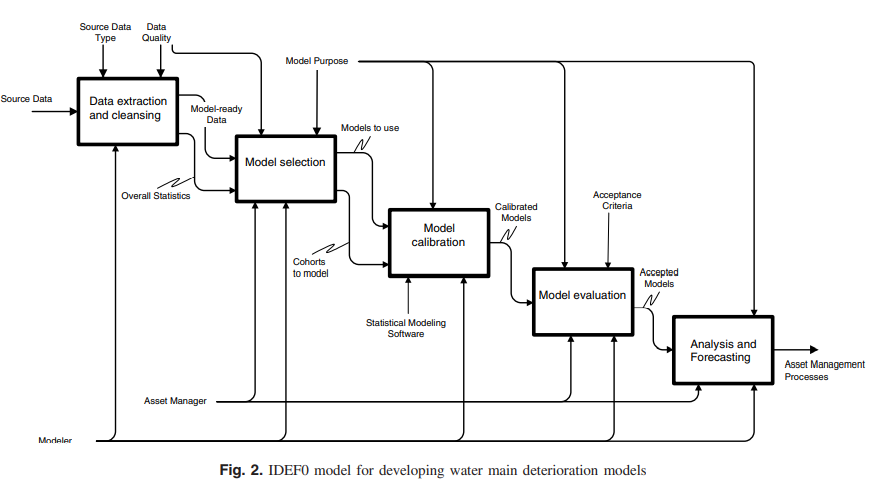
Comparison of statistical deterioration models for water distribution networks
The use of water main break history as a proxy for condition has become common practice because of the high costs associated with direct assessments. Statistical deterioration models predict future water main breaks on the basis of historical patterns. Many municipalities are beginning to understand the value of utilizing water pipe break histories to manage their noncritical distribution networks via deterioration models. This paper presents a generic IDEF0 process model for developing water main deterioration models. Two common statistical deterioration models for water pipes are compared
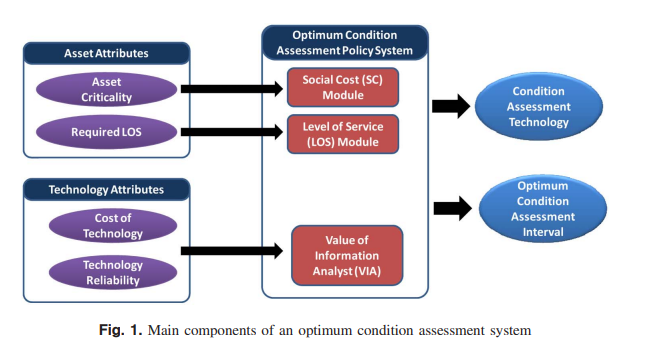
Optimizing inspection policies for buried municipal pipe infrastructure
Condition assessment is an integral component in any infrastructure asset management system. Without condition information, asset managers lack the ability to make appropriate decisions regarding needed maintenance, rehabilitation, and replacement of infrastructure. Existing and emerging technologies for assessing the condition of water and sewer pipes provide a better picture of the state of these buried assets. Unfortunately, many of these technologies are costly and provide results that are not always highly reliable. This paper presents a methodology to assist asset managers in balancing
Discrete event simulation tool for earthmoving fleet selection
Earthmoving operations represent a sizable work in heavy civil engineering projects. Selecting optimum fleet configuration for an earthmoving operation is a very difficult process, especially when dealing with a multi loader type and multi truck type configurations. This paper presents a framework that can be used for the selection of optimum fleet for earthmoving operations. It enables the user to input the available loading and hauling equipment, then, it calculates the cost and total project time of each possible fleet combination, and finally it provides a list of the top-ten best fleet
Knowledge management in contract administration: An ontological engineering approach
Knowledge has been identified to be a significant organizational resource, which if used effectively can provide competitive advantage. Construction contract administration is a complex, knowledge-intensive process that if properly managed can mitigate the contractor's risk exposure. Challenges in proper knowledge management of contract administration are due to: 1) Large amount of fragmented information that is required to manage a construction contract, 2) Information located in heterogeneous sources (Request For Information (RFIs), site notices, schedules, contracts, etc...), 3) Information
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
