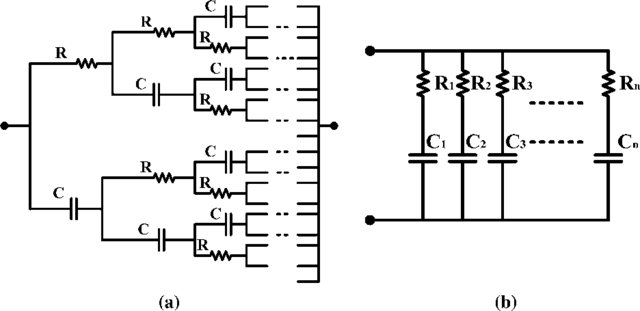
Using Meta-heuristic Optimization to Extract Bio-impedance Parameters from an Oscillator Circuit
This paper introduces a method for extracting the Cole-impedance model parameters using a meta-heuristic optimization technique. The method is based on a single proposed resistor controlled oscillator (SRCO) where the unknown bio-impedance is embedded. At two different oscillation frequencies, the start-up oscillation condition is recorded. Then the corresponding nonlinear equations are solved using the flower pollination optimization (FPA) technique to find the optimum impedance parameters that minimize an objective error function. Experimental results are provided, and comparisons with model
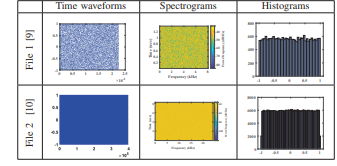
Speech Encryption on FPGA Using a Chaotic Generator and S-Box Table
In this paper, we proposed a new technique for designing a dynamic S-box depended on the idea of DNA module and Chaotic system to increase its security. Lorenz chaotic generator is utilized as the chaos part of the proposed design. This design is Tested on the Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) for the use of offline speech encryption and decryption in real time. The experimental results are presented on the oscilloscope. The security of the system is also validated through tests on Matlab. © 2019 IEEE.
Energy Harvesting Schemes for Wearable Devices
For the specifications of Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs), eHealth systems, and wearable devices, batteries are not desirable. They maximize the sensor nodes’ size and need to be replaced every few years through human interference. Energy harvesting is now being studied as the primary source of electricity for wearable devices. Several initiatives have succeeded in using energy harvesting to operate the wearable devices’ electronic components. However, to rely primarily on energy harvesting in wearable devices, some obstacles need to be addressed. This work surveys the development of
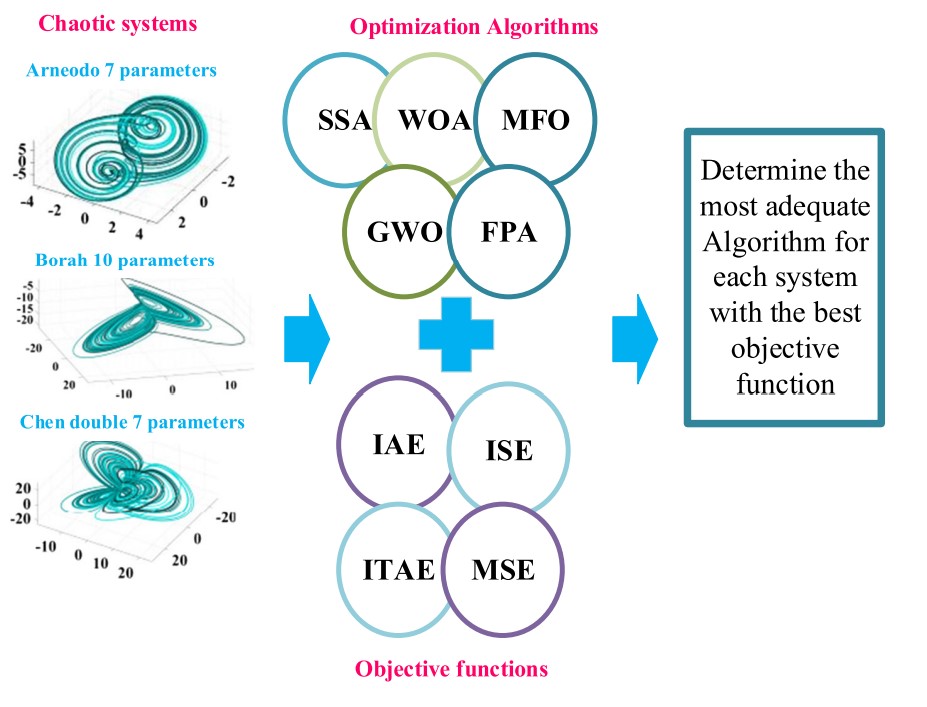
Parameter identification of fractional-order chaotic systems using different Meta-heuristic Optimization Algorithms
Fractional-order chaotic systems (FOCS) parameter identification is an essential issue in chaos control and synchronization process. In this paper, different recent Meta-heuristic Optimization Algorithms are used to estimate the parameters and orders of three FOCS. The investigated systems are Arneodo, Borah rotational attractor and Chen double- and four-wing systems. The employed algorithms are the Salp Swarm Algorithm, Whale Optimization Algorithm, Moth-Flame Optimizer, Grey Wolf Optimizer and the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). The proposed algorithms are applied on several objective
Two-port two impedances fractional order oscillators
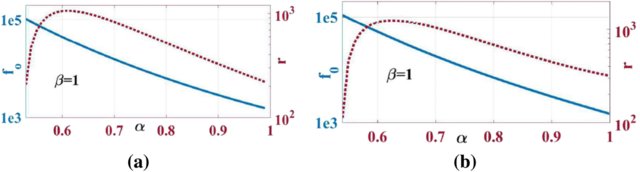
This paper presents a study for general fractional order oscillator based on two port network where two topologies of oscillator structure with two impedances are discussed. The two impedances are chosen to be fractional elements which give four combinations for each topology. The general oscillation frequency, condition and the phase difference between the two oscillatory outputs are deduced in terms of the transmission matrix parameter of a general two port network. As a case study: two different networks are presented which are op-amp based circuit and non-ideal gyrator circuit. The
Fractional-order Nonminimum-phase Filter Design
This paper introduces the design procedure of the fractional-order Soliman Nonminimum-phase filter. Theoretical analysis has been carried out providing the critical frequencies of the filter. The effect of fractional-order parameter \alpha on the filter response has been investigated. Additionally, two different approximation techniques (Oustaloup and Matsuda) have been employed to realize the filter. A comparison is held between the exact and approximated solutions. Theoretical analysis is verified through circuit simulations and experimental work. © 2019 IEEE.
Fractional-Order Relaxation Oscillators Based on Op-Amp and OTRA
This paper introduces closed formulas of two topologies of fractional-order relaxation oscillators. One of these topologies is based on Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) and the other one depends on Operational Operational Trans-Resistance Amplifier (OTRA). Special cases for each topology are also provided. The advantage of these designs comes from the added extra degree of freedom presented by the fractional-order α. Matsuda's approximation of sα is used to implement fractional-order capacitors. Also, experimental work is included to verify the theoretical results. © 2018 IEEE.
Comparison between three approximation methods on oscillator circuits
The promising capabilities of fractional-order devices challenge researchers to find a way to build it physically. Approximating the Laplacian operator sα can pave the way to emulate the fractional-order devices till its off-the-shelf appearance. This paper introduces three approximations of the Laplacian operator sα: Oustaloup, Matsuda, and Valsa by comparing their behaviors through two types of oscillator circuits. The first two are well-established approximations and the latter is proposed for the first time by converting its model network to an integer polynomial approximation of the
FPGA Implementation of X- and Heart-shapes Controllable Multi-Scroll Attractors
This paper proposes new multi-scrolls chaotic systems which is called the X-shape. The purpose is to have more complex systems and flexible ranges of the chaotic behavior. The proposed X-shape is a combination between V-shape and Λ-shape. This paper also represents the Heart-shape which considered a special case of the X-shape. The system complexity has been measured by MLE and compared with V-shape system. It shows lager MLE on the side of X-shape. In addition, the effect of changing system parameters has been discussed and compared with V-shape. Finally, a fully hardware implantation on FPGA
Biological inspired optimization algorithms for cole-impedance parameters identification
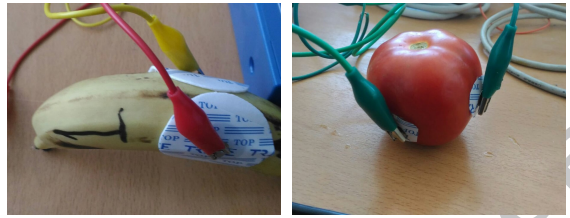
This paper introduces new meta-heuristic optimization algorithms for extracting the parameters of the Cole-impedance model. It is one of the most important models providing best fitting with the measured data. The proposed algorithms inspired by nature are known as Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA) and Moth-Flame Optimizer (MFO). The algorithms are tested over sets of both simulated and experimental data. The results are compared with other fitting algorithms such as the Non-linear least square (NLS) and Bacterial Foraging Optimization (BFO). The comparison showed a better fit in the sum of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
