A novel proximity based trust model for opportunistic networks
Trust should be earned. This is a famous quote that we use everyday implicitly or explicitly. Trust often is an inherent characteristic of our daily life, but in the digital community and between devices how can we represent trust? Since our mobile and digital devices became our confidants, we cannot share the information embedded in these devices with other devices without establishing trust. Hence, in this research a proximity based trust model based on Homophily principle is proposed. Earlier social studies have shown that people tend to have similarities with others in close proximity. In
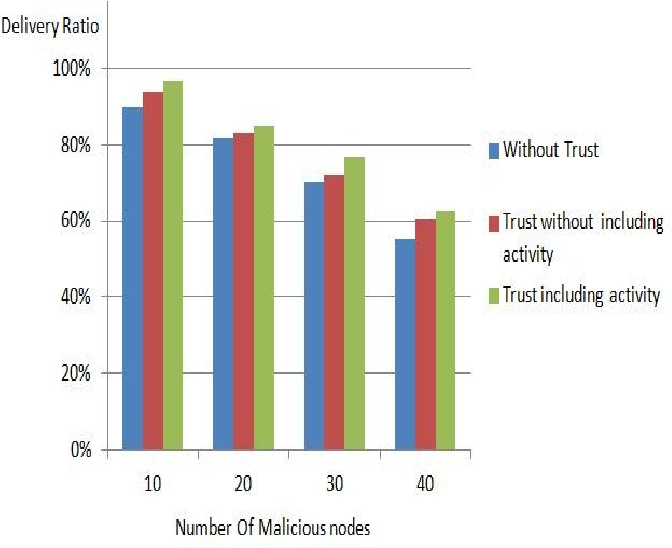
SAODV and modified SAODV performance comparison
Routing plays a vital role in ad hoc networks and Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV) protocol is considered one of the most famous routing protocols in ad hoc networks. Unfortunately it doesn't specify security measures. This has motivated the researchers to design secured version of AODV. However Security always collides with performance. The higher the security level is, the lower the performance level. This paper presents a performance comparison between Secure AODV (SAODV) and Modified SAODV (MSAODV). © 2013 IEEE.
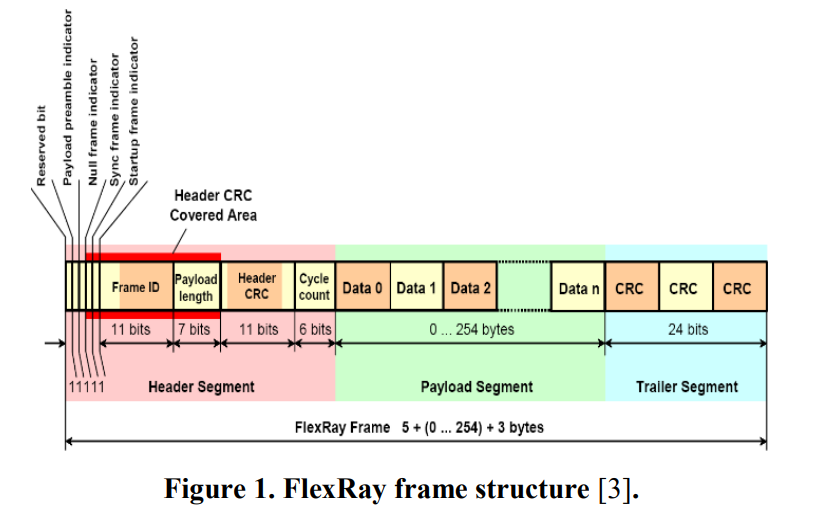
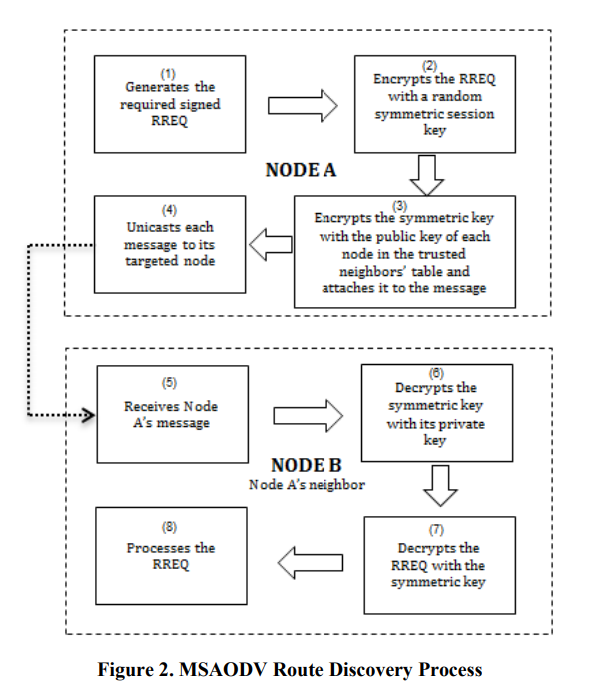
Lightweight authentication protocol deployment over FlexRay
In-vehicle network security is becoming a major concern for the automotive industry. Although there is significant research done in this area, there is still a significant gap between research and what is actually applied in practice. Controller area network (CAN) gains the most concern of community but little attention is given to FlexRay. Many signs indicate the approaching end of CAN usage and starting with other promising technologies. FlexRay is considered one of the main players in the near future. We believe that migration era is near enough to change our mindset in order to supply
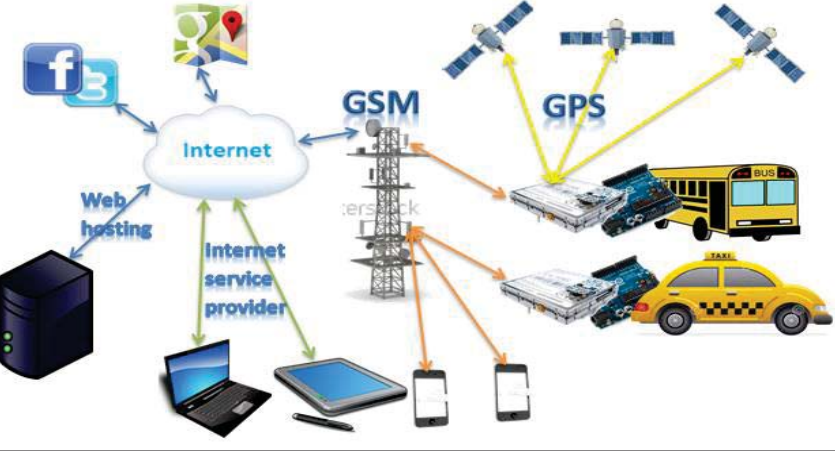
A Real-Time Social Network- Based Traffic Monitoring Vehicle Tracking System
Social networking has become an essential part of our daily lives. tTe integration of social networking communication model and Internet of Things (IoT) provides the users with a greater advantage than the benefit of using each one alone. This paper presents a real-time traffic monitoring and vehicle tracking for the public or private transportation sectors. The proposed system uses a social network service to provide traffic monitoring for individual users. A fully functional prototype model is developed and presented to demonstrate the system operation and to evaluate its performance. © 2018
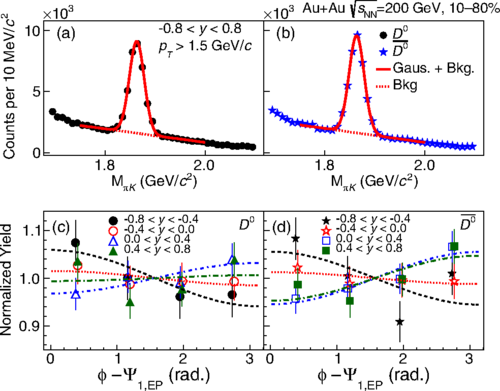
First Observation of the Directed Flow of D0 and D0 ̄ in Au+Au Collisions at sNN =200 GeV
We report the first measurement of rapidity-odd directed flow (v1) for D0 and D0̄ mesons at midrapidity (|y|
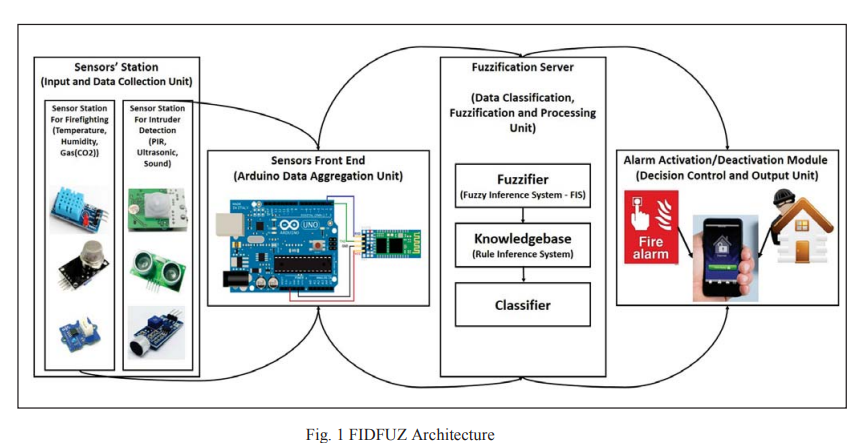
Design and implementation of robust firefighting/intruder detection system using fuzzy logic decision control (FIDFUZ)
This research focuses on using quantifiable methods for using the IoT as a main support to firefighting/intruder detection. From our research, we have found numerous researches associated to supplying remote services by means of portable sensors and communication technologies. We represent in our research a unique Smart Firefighting/lntruder Detection System with the support of Fuzzy Logic Decision Control (FIDFUZ). The projected system has an innovative value which is the Fuzzy Logic Decision Support System application that deals with the predicted inaccuracy and the doubt in the sensor's

Machine learning methodologies in Brain-Computer Interface systems
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a one kind of communication system that enables control of devices or communication with others only through brain signal activities without using motor activities. The main application for BCI is to provide an alternative channel for helping disabled persons, hereafter mentioned as subjects, to communicate with the external world. This paper tries to demonstrate the performance of different machine learning algorithms based on classification accuracy. Performance has been evaluated on dataset II from BCI Competition III for the year 2004 for two subjects 'A'

Modeling intrastromal photorefractive keratectomy procedures
The main idea to correct sight disorders using lasers is to modify corneal curvature by applying laser to specific layers of the cornea. Intrastromal Photorefractive keratectomy is a laser technique used to correct sight disorders by evaporating corneal tissue, which results in small cavities that may coincide to form a larger cavity that will collapse to deform the curvature of the cornea. In this work, a 3D finite element model of the cornea was designed with typical parameters to simulate the procedure. The model outcome was compared with an earlier 2D model used for the same purpose, so as
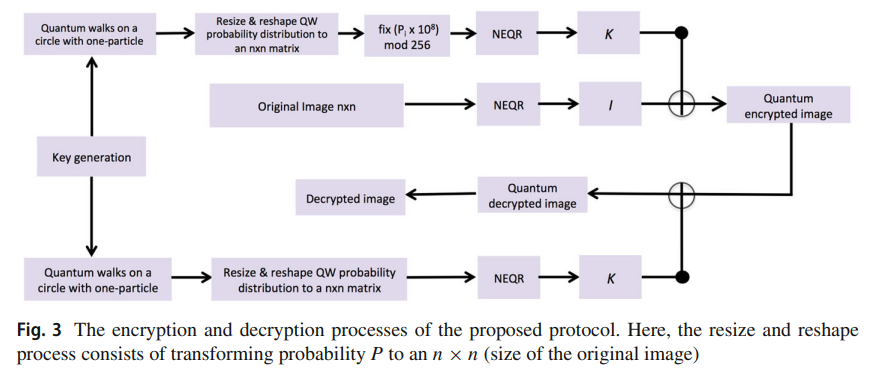
An encryption protocol for NEQR images based on one-particle quantum walks on a circle
Quantum walks are generalizations of random walks that have extensive applications in various fields including cryptography, quantum algorithms, and quantum networking. Discrete quantum walks can be seen as nonlinear mappings between quantum states and position probability distributions, and this mathematical property may be thought of as an imprint of chaotic behavior and consequently used to generate encryption keys. In this paper, we introduce encryption and decryption algorithms for NEQR images based on discrete quantum walks on a circle. We present full quantum circuits of proposed

Fuzzy gaussian process classification model
Soft labels allow a pattern to belong to multiple classes with different degrees. In many real world applications the association of a pattern to multiple classes is more realistic; to describe overlap and uncertainties in class belongingness. The objective of this work is to develop a fuzzy Gaussian process model for classification of soft labeled data. Gaussian process models have gained popularity in the recent years in classification and regression problems and are example of a flexible, probabilistic, non-parametric model with uncertainty predictions. Here we derive a fuzzy Gaussian model
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
