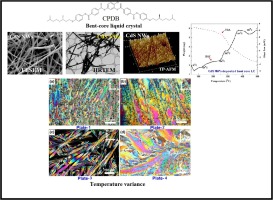
Reliable optoelectronic switchable device implementation by CdS nanowires conjugated bent-core liquid crystal matrix
Enhancing the performance of high luminescent and dielectrically capable cadmium sulfide nanowire (CdS NW) is of great importance, because of their promising ability in analyzing the dimensionality and size. The tuned physical characteristics of semiconductor CdS NWs allowed the manipulation of both electronic and optoelectronic devices at the nanoscale by dispersing a new bent core (BC) liquid crystal (LC) compound. This was derived from a 4-chlororesorcinol central core unit with two terephthalate based rod-like units carrying chiral (S)-3, 7-dimethyloctyloxy (namely ‘CPDB’) terminal chains
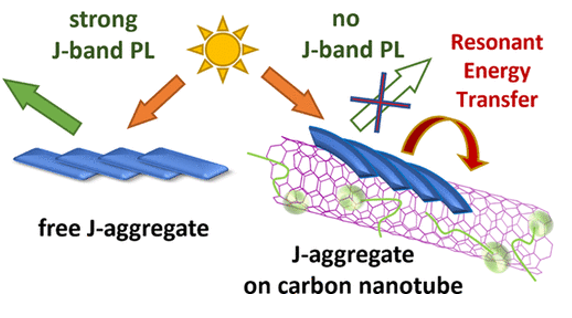
J-aggregates of amphiphilic cyanine dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: A combination between computational chemistry and experimental device physics
We report on the design and structure principles of 5,5′-6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′-dioctyl-3,3′-bis-(3-carboxypropyl)-benzimidacarbocyanine (Dye 1). Such metal-free amphiphilic cyanine dyes have many applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. AFM surface topographic investigation of amphiphilic molecules of Dye 1 adsorbed on TiO2 anode reveals the ability of spontaneous self-organization into highly ordered aggregates of fiber-like structure. These aggregates are known to exhibit outstanding optical properties of J-aggregates, namely, efficient exciton coupling and fast exciton energy migration
Real-time 4-way Intersection Smart Traffic Control System
Since traffic congestion is becoming a regular part of commuters' life, there is a pressing need for better traffic management. Most current traffic control systems are not sensitive to the current state of the roads being controlled, instead they are fixed, timed traffic signals that do not respond to unpredicted congestion. Solutions have been proposed to solve this problem including creating a large database for each traffic stop and determining the optimal traffic signals for the best vehicle flow based on the statistics collected, which does not react to data outliers. Other solutions
Association between long noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 and microRNA-377 in vitiligo
Background: Taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) is one of the long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) that plays a role in melanogenesis. MicroRNA-377 (miRNA-377) is a conserved noncoding RNA that regulates angiogenesis and promotes oxidative stress. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are components of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. PPAR-γ activators stimulate melanogenesis. Interleukin (IL)-17 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several immunological diseases. This work aimed at detecting the expression levels of lncRNA TUG1, miRNA-377, PPAR-γ, and IL-17 among vitiligo
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 58
